Passé Composé (Present Perfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb contre-passer
Introduction to the verb contre-passer
The English translation of the French verb contre-passer is “to counterbalance” or “to offset.” It is pronounced as “kon-truh-pa-sey,” with the stress on the second syllable.
The word contre-passer is derived from the French words “contre” meaning “against” and “passer” meaning “to pass.” It can be used as a transitive verb, meaning it requires a direct object, or as a reflexive verb, meaning the subject and object are the same.
In the Passé Composé tense, contre-passer is used to indicate an action that has been completed in the past and has had a counterbalancing effect on something else.
Here are three examples of contre-passer in the Passé Composé tense with their English translations:
- J’ai contre-passé mes dépenses avec mes économies. (I have offset my expenses with my savings.)
- Nous nous sommes contre-passés pour ne pas payer trop d’impôts. (We have counterbalanced each other to avoid paying too much taxes.)
- Les effets de la crise économique se sont contre-passés sur les petites entreprises. (The effects of the economic crisis have offset small businesses.)
In these examples, contre-passer is used to describe actions that have been completed in the past and have had a balancing effect on something else. It is commonly used in financial and economic contexts, but can also be used in other situations where there is a counterbalancing or offsetting effect.
Table of the Passé Composé (Present Perfect) Tense Conjugation of contre-passer
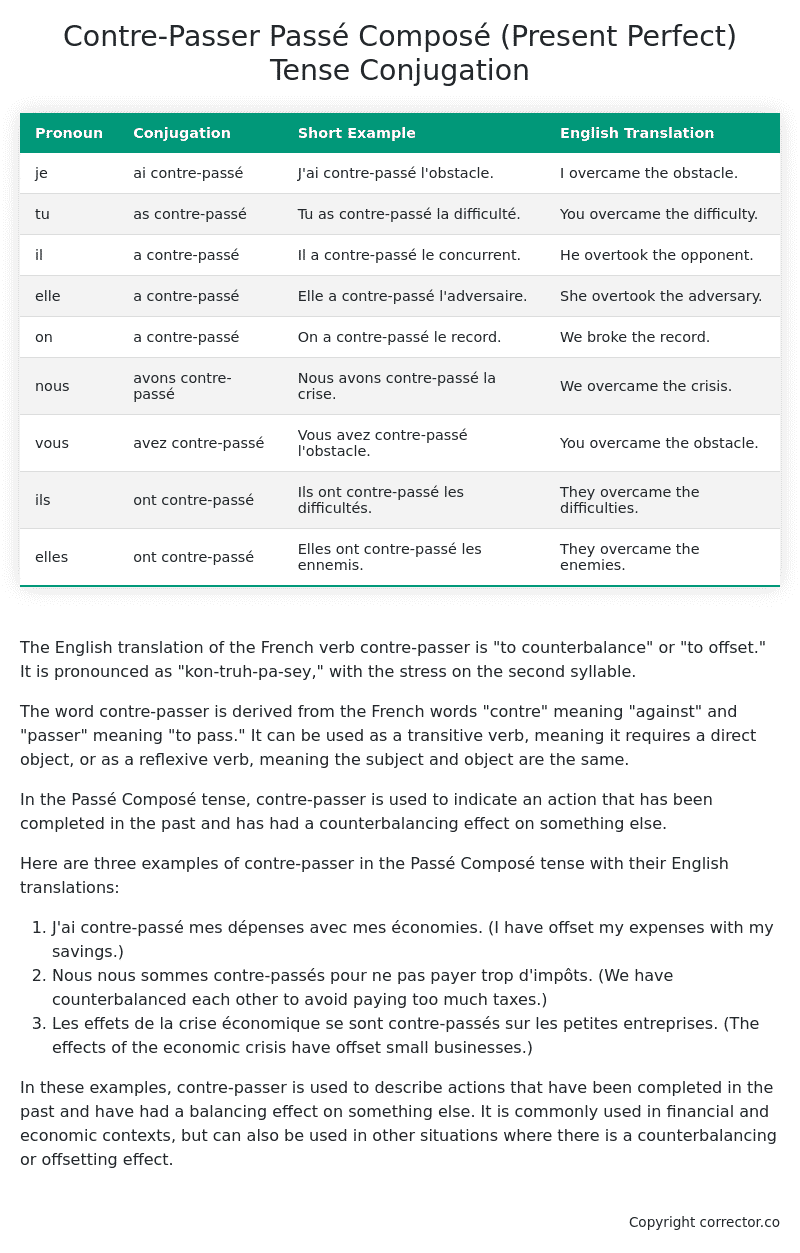
| Pronoun | Conjugation | Short Example | English Translation |
|---|---|---|---|
| je | ai contre-passé | J’ai contre-passé l’obstacle. | I overcame the obstacle. |
| tu | as contre-passé | Tu as contre-passé la difficulté. | You overcame the difficulty. |
| il | a contre-passé | Il a contre-passé le concurrent. | He overtook the opponent. |
| elle | a contre-passé | Elle a contre-passé l’adversaire. | She overtook the adversary. |
| on | a contre-passé | On a contre-passé le record. | We broke the record. |
| nous | avons contre-passé | Nous avons contre-passé la crise. | We overcame the crisis. |
| vous | avez contre-passé | Vous avez contre-passé l’obstacle. | You overcame the obstacle. |
| ils | ont contre-passé | Ils ont contre-passé les difficultés. | They overcame the difficulties. |
| elles | ont contre-passé | Elles ont contre-passé les ennemis. | They overcame the enemies. |
Other Conjugations for Contre-Passer.
Le Present (Present Tense) Conjugation of the French Verb contre-passer
Imparfait (Imperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb contre-passer
Passé Simple (Simple Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb contre-passer
Passé Composé (Present Perfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb contre-passer (this article)
Futur Simple (Simple Future) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb contre-passer
Futur Proche (Near Future) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb contre-passer
Plus-que-parfait (Pluperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb contre-passer
Passé Antérieur (Past Anterior) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb contre-passer
Futur Antérieur (Future Anterior) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb contre-passer
Subjonctif Présent (Subjunctive Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb contre-passer
Subjonctif Passé (Subjunctive Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb contre-passer
Subjonctif Imparfait (Subjunctive Imperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb contre-passer
Conditionnel Présent (Conditional Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb contre-passer
Conditionnel Passé (Conditional Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb contre-passer
L’impératif Présent (Imperative Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb contre-passer
L’infinitif Présent (Infinitive Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb contre-passer
Struggling with French verbs or the language in general? Why not use our free French Grammar Checker – no registration required!
Get a FREE Download Study Sheet of this Conjugation 🔥
Simply right click the image below, click “save image” and get your free reference for the contre-passer present perfect tense conjugation!
Contre-Passer – About the French Passé Composé (Present Perfect) Tense
Formation of the Passé Composé
Set the auxiliary verb with either
Conjugate the auxiliary verb
Add the past participle
Common everyday usage patterns
Narrating Past Events
Sequential Actions
Describing Completed Actions
Interactions with other tenses
Imperfect Tense
Conditional and Future Tenses
Summary
I hope you enjoyed this article on the verb contre-passer. Still in a learning mood? Check out another TOTALLY random French verb conjugation!


