Passé Simple (Simple Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb caver
Introduction to the verb caver
The English translation of the French verb “caver” is “to cave in” or “to give in.” The infinitive form of “caver” is pronounced as [ka-veh].
The verb “caver” has its origins in the Latin word “cavare,” which means “to hollow out.” In everyday French, “caver” is most often used in the Passé Simple tense, which is a literary past tense used in formal or written French.
Here are three simple examples of “caver” in the Passé Simple tense, along with their English translations:
- Il cava devant l’adversité. (He caved in front of adversity.)
- Nous avons beaucoup travaillé jusqu’à ce que nous cavâmes. (We worked hard until we caved in.)
- Les protestataires ne cavèrent pas face aux pressions. (The protesters didn’t cave in under pressure.)
In these examples, “caver” is used to express giving in, surrendering, or yielding in different contexts.
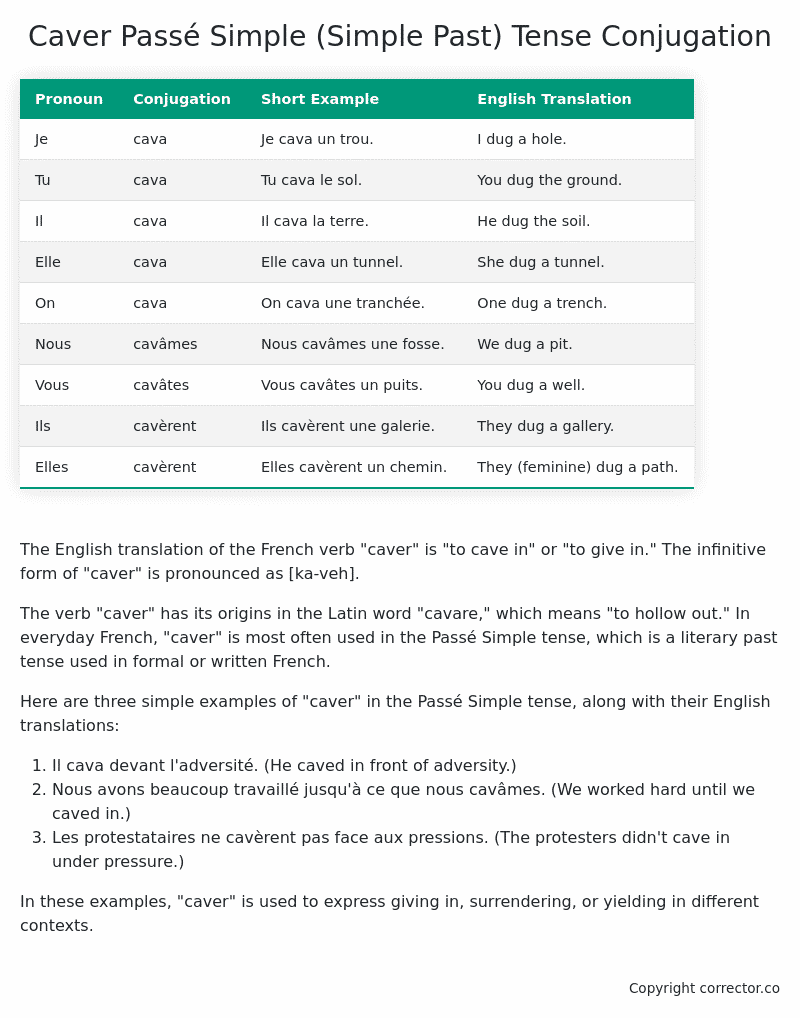
Table of the Passé Simple (Simple Past) Tense Conjugation of caver
| Pronoun | Conjugation | Short Example | English Translation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Je | cava | Je cava un trou. | I dug a hole. |
| Tu | cava | Tu cava le sol. | You dug the ground. |
| Il | cava | Il cava la terre. | He dug the soil. |
| Elle | cava | Elle cava un tunnel. | She dug a tunnel. |
| On | cava | On cava une tranchée. | One dug a trench. |
| Nous | cavâmes | Nous cavâmes une fosse. | We dug a pit. |
| Vous | cavâtes | Vous cavâtes un puits. | You dug a well. |
| Ils | cavèrent | Ils cavèrent une galerie. | They dug a gallery. |
| Elles | cavèrent | Elles cavèrent un chemin. | They (feminine) dug a path. |
Other Conjugations for Caver.
Le Present (Present Tense) Conjugation of the French Verb caver
Imparfait (Imperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb caver
Passé Simple (Simple Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb caver (You’re reading it right now!)
Passé Composé (Present Perfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb caver
Futur Simple (Simple Future) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb caver
Futur Proche (Near Future) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb caver
Plus-que-parfait (Pluperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb caver
Passé Antérieur (Past Anterior) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb caver
Futur Antérieur (Future Anterior) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb caver
Subjonctif Présent (Subjunctive Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb caver
Subjonctif Passé (Subjunctive Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb caver
Subjonctif Imparfait (Subjunctive Imperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb caver
Subjonctif Plus-que-parfait (Subjunctive Pluperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb caver
Conditionnel Présent (Conditional Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb caver
Conditionnel Passé (Conditional Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb caver
Conditionnel Passé II (Conditional Past II) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb caver
L’impératif Présent (Imperative Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb caver
L’impératif Passé (Imperative Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb caver
L’infinitif Présent (Infinitive Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb caver
L’infinitif Passé (Infinitive Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb caver
Le Participe Présent (Present Participle) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb caver
Le Participe Passé (Past Participle) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb caver
Struggling with French verbs or the language in general? Why not use our free French Grammar Checker – no registration required!
Get a FREE Download Study Sheet of this Conjugation 🔥
Simply right click the image below, click “save image” and get your free reference for the caver Passé Simple tense conjugation!
Caver – About the French Passé Simple (Simple Past) Tense
Formation
Usage
Narration
Historical Context
Interactions with other tenses
Passé Composé
Imparfait
Conditional and Subjunctive
Summary
I hope you enjoyed this article on the verb caver. Still in a learning mood? Check out another TOTALLY random French verb conjugation!


