Passé Simple (Simple Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb chosifier
Introduction to the verb chosifier
The English translation of the French verb “chosifier” is “to objectify.” The infinitive form of “chosifier” is pronounced as “sho-zee-fie”.
“Chosifier” comes from the noun “chose,” meaning “thing” or “object.” The verb “chosifier” is derived from this noun and refers to the action of turning something into an object, treating someone or something as a mere thing.
In everyday French, the Passé Simple tense is rarely used in spoken language but is commonly found in written literature or formal texts. However, “chosifier” is not a frequently used verb, and it is even less common to find it in the Passé Simple tense. Nonetheless, here are three examples of its usage in the Simple Past tense:
-
Il chosifia la femme en ne la considérant que comme un objet de désir.
(He objectified the woman by considering her only as an object of desire.) -
L’écrivain chosifiait ses personnages, les décrivant uniquement par leurs apparences physiques.
(The writer objectified his characters, describing them solely through their physical appearances.) -
Pendant des années, la société a chosifié les travailleurs en ne les reconnaissant que comme des outils de production.
(For years, society objectified workers by recognizing them solely as production tools.)
Please note that the usage of “chosifier” in the Passé Simple tense is quite rare, and it is more commonly used in other tenses such as the present or the past compound.
Table of the Passé Simple (Simple Past) Tense Conjugation of chosifier
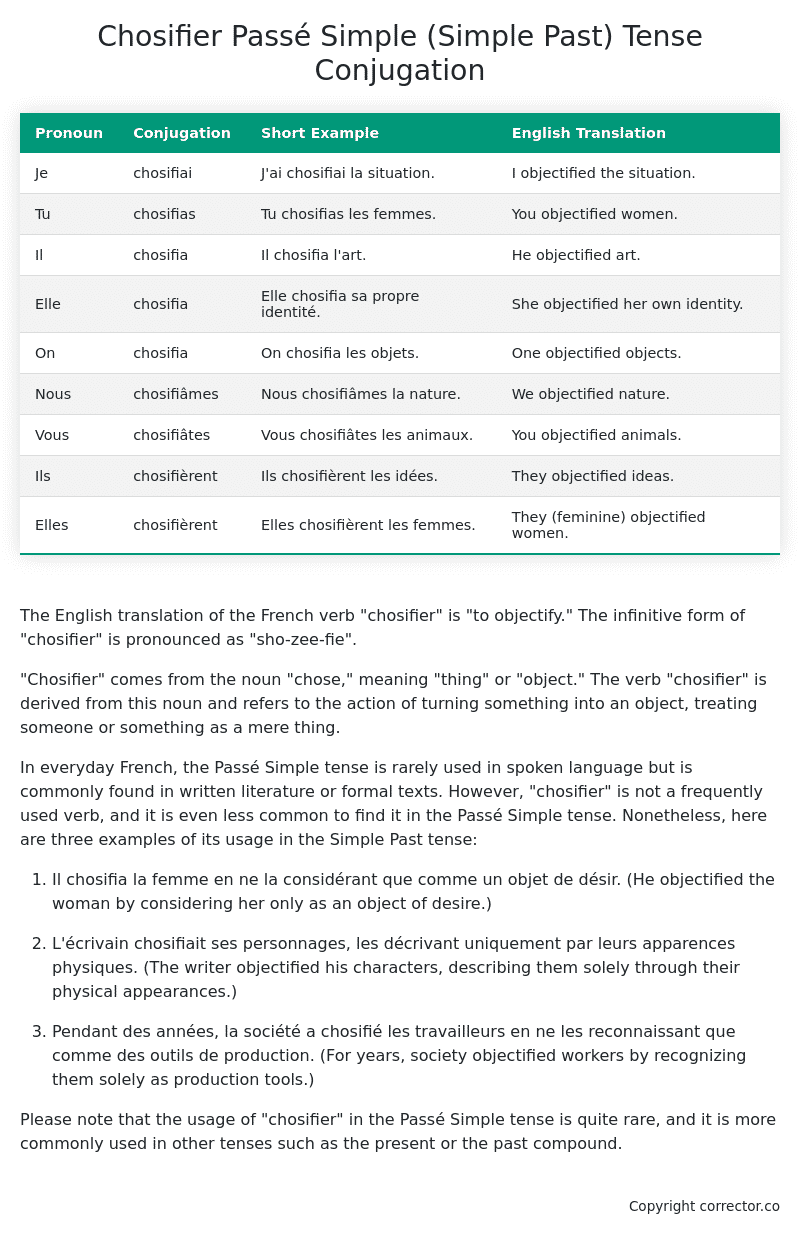
| Pronoun | Conjugation | Short Example | English Translation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Je | chosifiai | J’ai chosifiai la situation. | I objectified the situation. |
| Tu | chosifias | Tu chosifias les femmes. | You objectified women. |
| Il | chosifia | Il chosifia l’art. | He objectified art. |
| Elle | chosifia | Elle chosifia sa propre identité. | She objectified her own identity. |
| On | chosifia | On chosifia les objets. | One objectified objects. |
| Nous | chosifiâmes | Nous chosifiâmes la nature. | We objectified nature. |
| Vous | chosifiâtes | Vous chosifiâtes les animaux. | You objectified animals. |
| Ils | chosifièrent | Ils chosifièrent les idées. | They objectified ideas. |
| Elles | chosifièrent | Elles chosifièrent les femmes. | They (feminine) objectified women. |
Other Conjugations for Chosifier.
Le Present (Present Tense) Conjugation of the French Verb chosifier
Imparfait (Imperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb chosifier
Passé Simple (Simple Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb chosifier (You’re reading it right now!)
Passé Composé (Present Perfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb chosifier
Futur Simple (Simple Future) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb chosifier
Futur Proche (Near Future) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb chosifier
Plus-que-parfait (Pluperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb chosifier
Passé Antérieur (Past Anterior) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb chosifier
Futur Antérieur (Future Anterior) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb chosifier
Subjonctif Présent (Subjunctive Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb chosifier
Subjonctif Passé (Subjunctive Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb chosifier
Subjonctif Imparfait (Subjunctive Imperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb chosifier
Subjonctif Plus-que-parfait (Subjunctive Pluperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb chosifier
Conditionnel Présent (Conditional Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb chosifier
Conditionnel Passé (Conditional Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb chosifier
Conditionnel Passé II (Conditional Past II) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb chosifier
L’impératif Présent (Imperative Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb chosifier
L’impératif Passé (Imperative Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb chosifier
L’infinitif Présent (Infinitive Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb chosifier
L’infinitif Passé (Infinitive Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb chosifier
Le Participe Présent (Present Participle) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb chosifier
Le Participe Passé (Past Participle) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb chosifier
Struggling with French verbs or the language in general? Why not use our free French Grammar Checker – no registration required!
Get a FREE Download Study Sheet of this Conjugation 🔥
Simply right click the image below, click “save image” and get your free reference for the chosifier Passé Simple tense conjugation!
Chosifier – About the French Passé Simple (Simple Past) Tense
Formation
Usage
Narration
Historical Context
Interactions with other tenses
Passé Composé
Imparfait
Conditional and Subjunctive
Summary
I hope you enjoyed this article on the verb chosifier. Still in a learning mood? Check out another TOTALLY random French verb conjugation!


