Passé Simple (Simple Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb coïncider
Introduction to the verb coïncider
The English translation of the French verb coïncider is “to coincide.” The infinitive form is pronounced as “kwan-si-dey.”
Coïncider originates from the Latin word “coincidere,” which means “to fall together.” In everyday French, it is commonly used in the Passé Simple tense to express actions that occurred in the past with a certain degree of formality. However, it is important to note that the Passé Simple tense is rarely used in spoken French and is mainly found in written literature.
Here are three examples of coïncider in the Passé Simple tense, along with their English translations:
- Les réponses de Pierre coïncidèrent avec les miennes. (Pierre’s answers coincided with mine.)
- Nos vacances coïncidèrent avec le festival de musique. (Our vacation coincided with the music festival.)
- Leur arrivée coïncidit avec le début de la cérémonie. (Their arrival coincided with the beginning of the ceremony.)
In these examples, coïncider in the Passé Simple tense emphasizes a specific point in the past where two or more events aligned or happened simultaneously.
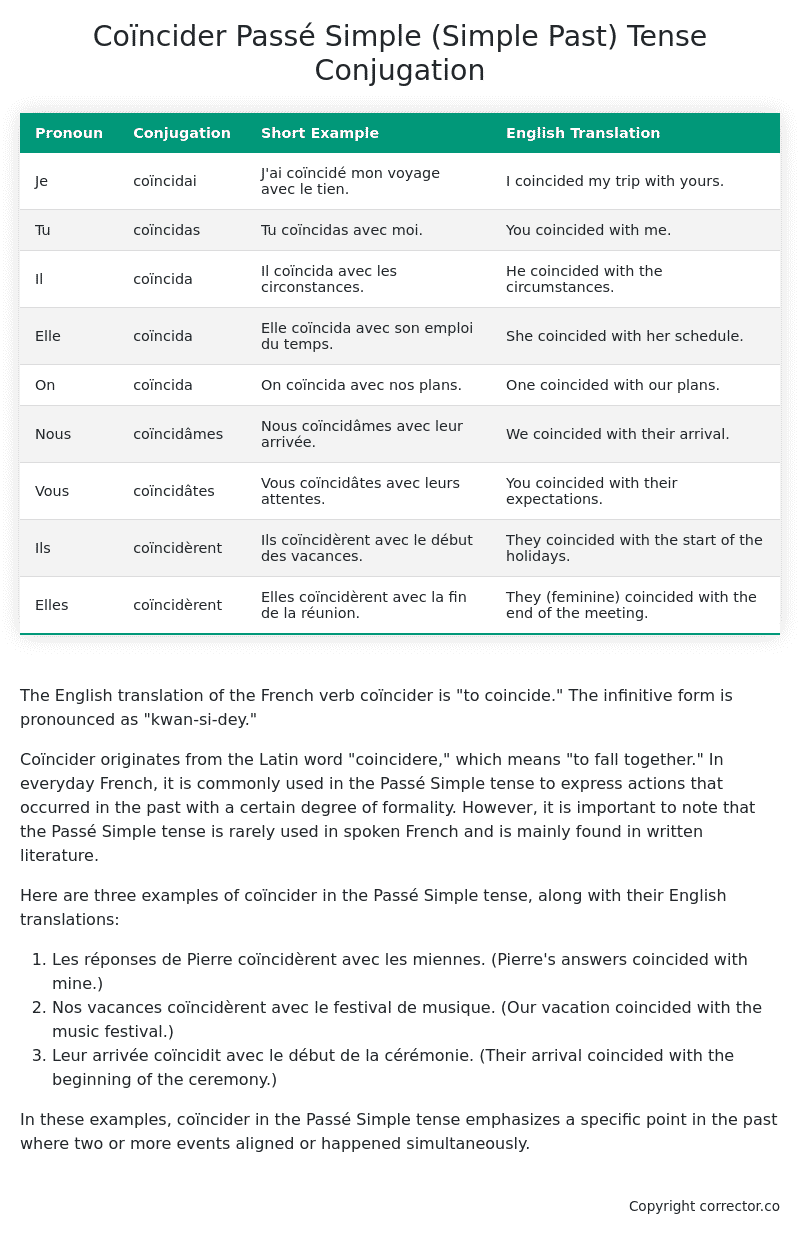
Table of the Passé Simple (Simple Past) Tense Conjugation of coïncider
| Pronoun | Conjugation | Short Example | English Translation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Je | coïncidai | J’ai coïncidé mon voyage avec le tien. | I coincided my trip with yours. |
| Tu | coïncidas | Tu coïncidas avec moi. | You coincided with me. |
| Il | coïncida | Il coïncida avec les circonstances. | He coincided with the circumstances. |
| Elle | coïncida | Elle coïncida avec son emploi du temps. | She coincided with her schedule. |
| On | coïncida | On coïncida avec nos plans. | One coincided with our plans. |
| Nous | coïncidâmes | Nous coïncidâmes avec leur arrivée. | We coincided with their arrival. |
| Vous | coïncidâtes | Vous coïncidâtes avec leurs attentes. | You coincided with their expectations. |
| Ils | coïncidèrent | Ils coïncidèrent avec le début des vacances. | They coincided with the start of the holidays. |
| Elles | coïncidèrent | Elles coïncidèrent avec la fin de la réunion. | They (feminine) coincided with the end of the meeting. |
Other Conjugations for Coïncider.
Le Present (Present Tense) Conjugation of the French Verb coïncider
Imparfait (Imperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb coïncider
Passé Simple (Simple Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb coïncider (You’re reading it right now!)
Passé Composé (Present Perfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb coïncider
Futur Simple (Simple Future) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb coïncider
Futur Proche (Near Future) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb coïncider
Plus-que-parfait (Pluperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb coïncider
Passé Antérieur (Past Anterior) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb coïncider
Futur Antérieur (Future Anterior) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb coïncider
Subjonctif Présent (Subjunctive Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb coïncider
Subjonctif Passé (Subjunctive Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb coïncider
Subjonctif Imparfait (Subjunctive Imperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb coïncider
Subjonctif Plus-que-parfait (Subjunctive Pluperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb coïncider
Conditionnel Présent (Conditional Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb coïncider
Conditionnel Passé (Conditional Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb coïncider
Conditionnel Passé II (Conditional Past II) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb coïncider
L’impératif Présent (Imperative Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb coïncider
L’impératif Passé (Imperative Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb coïncider
L’infinitif Présent (Infinitive Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb coïncider
L’infinitif Passé (Infinitive Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb coïncider
Le Participe Présent (Present Participle) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb coïncider
Le Participe Passé (Past Participle) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb coïncider
Struggling with French verbs or the language in general? Why not use our free French Grammar Checker – no registration required!
Get a FREE Download Study Sheet of this Conjugation 🔥
Simply right click the image below, click “save image” and get your free reference for the coïncider Passé Simple tense conjugation!
Coïncider – About the French Passé Simple (Simple Past) Tense
Formation
Usage
Narration
Historical Context
Interactions with other tenses
Passé Composé
Imparfait
Conditional and Subjunctive
Summary
I hope you enjoyed this article on the verb coïncider. Still in a learning mood? Check out another TOTALLY random French verb conjugation!


