Passé Simple (Simple Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb déjeuner
Introduction to the verb déjeuner
The English translation of the French verb “déjeuner” is “to have breakfast” or “to lunch.” The infinitive form, “déjeuner,” is pronounced as day-zheuh-nay.
The word “déjeuner” originates from the Latin word “disjejunare,” which means “to stop fasting.” In everyday French, it is most often used in the Passé Simple tense to refer to a past action completed in a formal or literary context.
Here are three examples of its usage in the Passé Simple tense along with their English translations:
-
Je déjeunai à sept heures du matin.
(I had breakfast at seven in the morning.) -
L’année dernière, nous déjeunâmes au restaurant durant nos vacances.
(Last year, we had lunch at the restaurant during our vacation.) -
Elle déjeuna avec ses amis avant de partir.
(She had breakfast with her friends before leaving.)
Table of the Passé Simple (Simple Past) Tense Conjugation of déjeuner
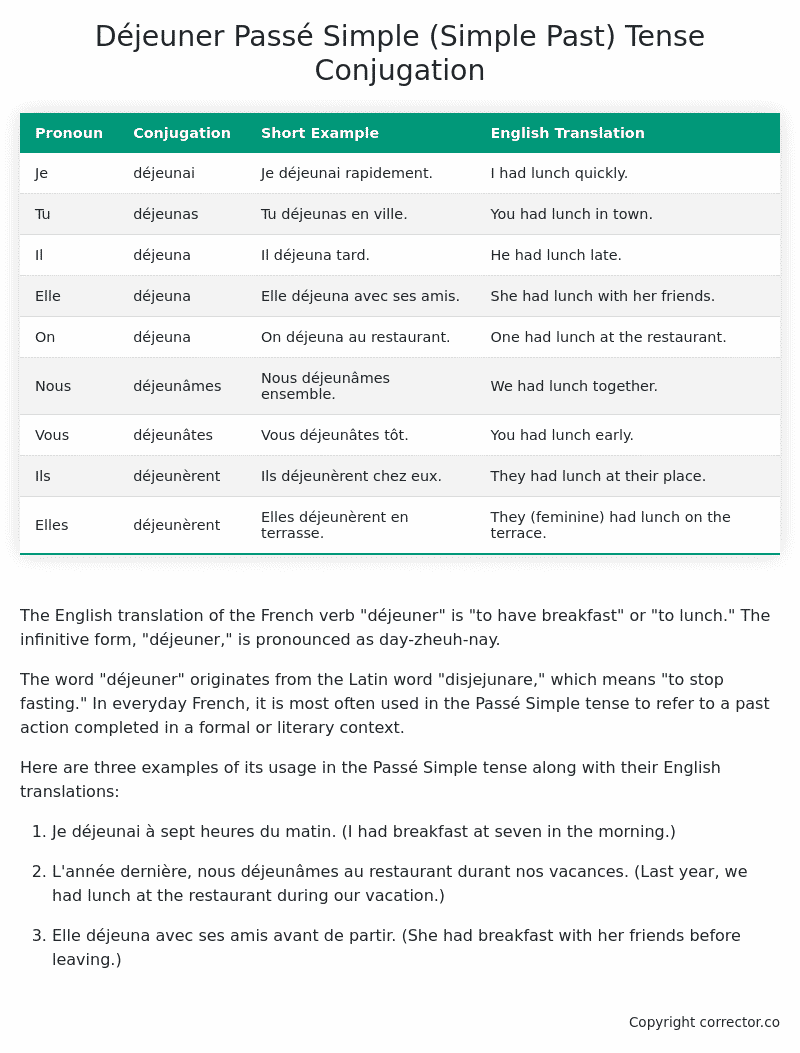
| Pronoun | Conjugation | Short Example | English Translation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Je | déjeunai | Je déjeunai rapidement. | I had lunch quickly. |
| Tu | déjeunas | Tu déjeunas en ville. | You had lunch in town. |
| Il | déjeuna | Il déjeuna tard. | He had lunch late. |
| Elle | déjeuna | Elle déjeuna avec ses amis. | She had lunch with her friends. |
| On | déjeuna | On déjeuna au restaurant. | One had lunch at the restaurant. |
| Nous | déjeunâmes | Nous déjeunâmes ensemble. | We had lunch together. |
| Vous | déjeunâtes | Vous déjeunâtes tôt. | You had lunch early. |
| Ils | déjeunèrent | Ils déjeunèrent chez eux. | They had lunch at their place. |
| Elles | déjeunèrent | Elles déjeunèrent en terrasse. | They (feminine) had lunch on the terrace. |
Other Conjugations for Déjeuner.
Le Present (Present Tense) Conjugation of the French Verb déjeuner
Imparfait (Imperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb déjeuner
Passé Simple (Simple Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb déjeuner (You’re reading it right now!)
Passé Composé (Present Perfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb déjeuner
Futur Simple (Simple Future) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb déjeuner
Futur Proche (Near Future) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb déjeuner
Plus-que-parfait (Pluperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb déjeuner
Passé Antérieur (Past Anterior) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb déjeuner
Futur Antérieur (Future Anterior) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb déjeuner
Subjonctif Présent (Subjunctive Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb déjeuner
Subjonctif Passé (Subjunctive Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb déjeuner
Subjonctif Imparfait (Subjunctive Imperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb déjeuner
Subjonctif Plus-que-parfait (Subjunctive Pluperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb déjeuner
Conditionnel Présent (Conditional Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb déjeuner
Conditionnel Passé (Conditional Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb déjeuner
Conditionnel Passé II (Conditional Past II) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb déjeuner
L’impératif Présent (Imperative Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb déjeuner
L’impératif Passé (Imperative Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb déjeuner
L’infinitif Présent (Infinitive Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb déjeuner
L’infinitif Passé (Infinitive Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb déjeuner
Le Participe Présent (Present Participle) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb déjeuner
Le Participe Passé (Past Participle) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb déjeuner
Struggling with French verbs or the language in general? Why not use our free French Grammar Checker – no registration required!
Get a FREE Download Study Sheet of this Conjugation 🔥
Simply right click the image below, click “save image” and get your free reference for the déjeuner Passé Simple tense conjugation!
Déjeuner – About the French Passé Simple (Simple Past) Tense
Formation
Usage
Narration
Historical Context
Interactions with other tenses
Passé Composé
Imparfait
Conditional and Subjunctive
Summary
I hope you enjoyed this article on the verb déjeuner. Still in a learning mood? Check out another TOTALLY random French verb conjugation!


