Plus-que-parfait (Pluperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb dénoter
Introduction to the verb dénoter
The English translation of the French verb dénoter is “to denote” or “to indicate.” It is pronounced “day-no-tay” in the infinitive form.
The word dénoter comes from the Latin word “denotare,” which means “to mark out.” It is most often used in everyday French to indicate or express something, usually through a symbol or sign. In the Plus-que-parfait tense, it is used to describe an action or event that had happened before another action or event in the past.
Here are three simple examples of dénoter in the Plus-que-parfait tense, with the respective English translations:
- J’avais dénoté un lien fort entre eux. (I had denoted a strong connection between them.)
- Il avait dénoté son mécontentement en soupirant. (He had denoted his dissatisfaction by sighing.)
- Elle avait dénoté un sourire sur son visage. (She had denoted a smile on her face.)
Table of the Plus-que-parfait (Pluperfect) Tense Conjugation of dénoter
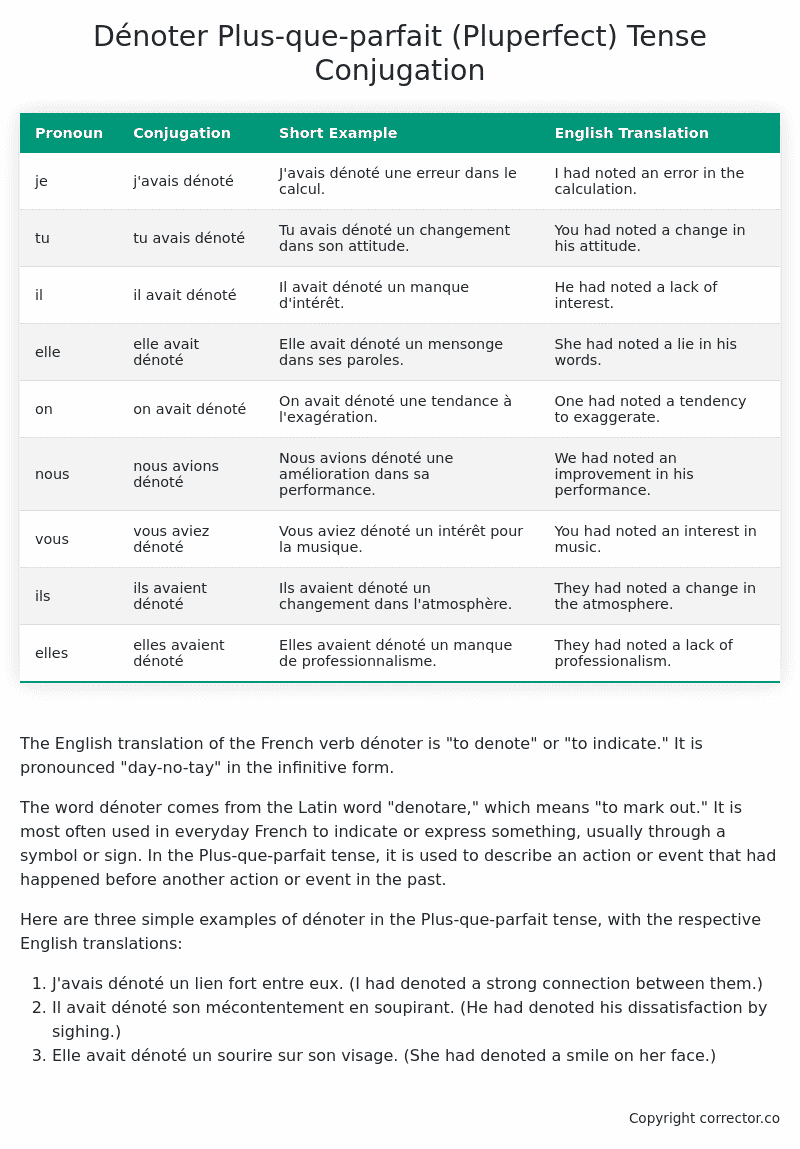
| Pronoun | Conjugation | Short Example | English Translation |
|---|---|---|---|
| je | j’avais dénoté | J’avais dénoté une erreur dans le calcul. | I had noted an error in the calculation. |
| tu | tu avais dénoté | Tu avais dénoté un changement dans son attitude. | You had noted a change in his attitude. |
| il | il avait dénoté | Il avait dénoté un manque d’intérêt. | He had noted a lack of interest. |
| elle | elle avait dénoté | Elle avait dénoté un mensonge dans ses paroles. | She had noted a lie in his words. |
| on | on avait dénoté | On avait dénoté une tendance à l’exagération. | One had noted a tendency to exaggerate. |
| nous | nous avions dénoté | Nous avions dénoté une amélioration dans sa performance. | We had noted an improvement in his performance. |
| vous | vous aviez dénoté | Vous aviez dénoté un intérêt pour la musique. | You had noted an interest in music. |
| ils | ils avaient dénoté | Ils avaient dénoté un changement dans l’atmosphère. | They had noted a change in the atmosphere. |
| elles | elles avaient dénoté | Elles avaient dénoté un manque de professionnalisme. | They had noted a lack of professionalism. |
Other Conjugations for Dénoter.
Le Present (Present Tense) Conjugation of the French Verb dénoter
Imparfait (Imperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb dénoter
Passé Simple (Simple Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb dénoter
Passé Composé (Present Perfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb dénoter
Futur Simple (Simple Future) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb dénoter
Futur Proche (Near Future) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb dénoter
Plus-que-parfait (Pluperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb dénoter (this article)
Passé Antérieur (Past Anterior) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb dénoter
Futur Antérieur (Future Anterior) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb dénoter
Subjonctif Présent (Subjunctive Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb dénoter
Subjonctif Passé (Subjunctive Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb dénoter
Subjonctif Imparfait (Subjunctive Imperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb dénoter
Subjonctif Plus-que-parfait (Subjunctive Pluperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb dénoter
Conditionnel Présent (Conditional Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb dénoter
Conditionnel Passé (Conditional Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb dénoter
L’impératif Présent (Imperative Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb dénoter
L’infinitif Présent (Infinitive Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb dénoter
Struggling with French verbs or the language in general? Why not use our free French Grammar Checker – no registration required!
Get a FREE Download Study Sheet of this Conjugation 🔥
Simply right click the image below, click “save image” and get your free reference for the dénoter Plus-que-parfait tense conjugation!
Dénoter – About the French Plus-que-parfait (Pluperfect) Tense
Tense Formation
Common everyday usage patterns
Sequencing of past events
Background information
Hypothetical or reported speech
Interactions with other tenses
Summary
I hope you enjoyed this article on the verb dénoter. Still in a learning mood? Check out another TOTALLY random French verb conjugation!


