Plus-que-parfait (Pluperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb discréditer
Introduction to the verb discréditer
The English translation of the French verb discréditer is “to discredit.” It is pronounced “dees-kreh-dee-tay.”
The word discréditer comes from the Latin word “discredere” which means “to disbelieve or distrust.” In French, it is most often used in everyday language to describe the act of damaging someone’s reputation or credibility.
In the Plus-que-parfait tense, discréditer is conjugated as “avais discrédité” for the first and second person singular, “avais discrédité” for the third person singular, and “avions discrédité” for the first person plural. It is formed by using the auxiliary verb “avoir” in the imperfect tense and adding the past participle “discrédité.”
Three simple examples of its usage in this tense are:
- J’avais discrédité ses propos en prouvant mes arguments. (I had discredited his statements by proving my arguments.)
- Tu avais discrédité notre équipe en manquant de fair-play. (You had discredited our team by lacking sportsmanship.)
- Ils avaient discrédité leur propre entreprise en mentant aux clients. (They had discredited their own company by lying to clients.)
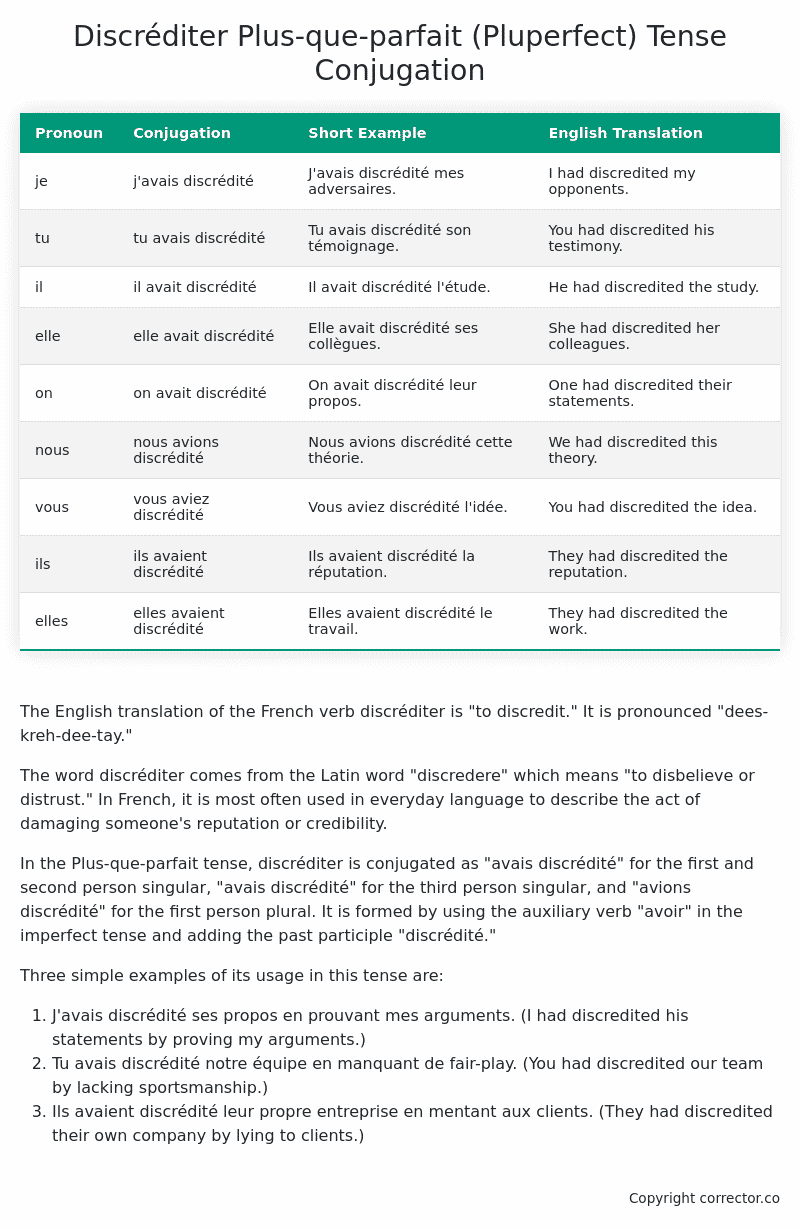
Table of the Plus-que-parfait (Pluperfect) Tense Conjugation of discréditer
| Pronoun | Conjugation | Short Example | English Translation |
|---|---|---|---|
| je | j’avais discrédité | J’avais discrédité mes adversaires. | I had discredited my opponents. |
| tu | tu avais discrédité | Tu avais discrédité son témoignage. | You had discredited his testimony. |
| il | il avait discrédité | Il avait discrédité l’étude. | He had discredited the study. |
| elle | elle avait discrédité | Elle avait discrédité ses collègues. | She had discredited her colleagues. |
| on | on avait discrédité | On avait discrédité leur propos. | One had discredited their statements. |
| nous | nous avions discrédité | Nous avions discrédité cette théorie. | We had discredited this theory. |
| vous | vous aviez discrédité | Vous aviez discrédité l’idée. | You had discredited the idea. |
| ils | ils avaient discrédité | Ils avaient discrédité la réputation. | They had discredited the reputation. |
| elles | elles avaient discrédité | Elles avaient discrédité le travail. | They had discredited the work. |
Other Conjugations for Discréditer.
Le Present (Present Tense) Conjugation of the French Verb discréditer
Imparfait (Imperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb discréditer
Passé Simple (Simple Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb discréditer
Passé Composé (Present Perfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb discréditer
Futur Simple (Simple Future) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb discréditer
Futur Proche (Near Future) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb discréditer
Plus-que-parfait (Pluperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb discréditer (this article)
Passé Antérieur (Past Anterior) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb discréditer
Futur Antérieur (Future Anterior) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb discréditer
Subjonctif Présent (Subjunctive Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb discréditer
Subjonctif Passé (Subjunctive Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb discréditer
Subjonctif Imparfait (Subjunctive Imperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb discréditer
Conditionnel Présent (Conditional Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb discréditer
Conditionnel Passé (Conditional Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb discréditer
L’impératif Présent (Imperative Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb discréditer
L’infinitif Présent (Infinitive Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb discréditer
Struggling with French verbs or the language in general? Why not use our free French Grammar Checker – no registration required!
Get a FREE Download Study Sheet of this Conjugation 🔥
Simply right click the image below, click “save image” and get your free reference for the discréditer Plus-que-parfait tense conjugation!
Discréditer – About the French Plus-que-parfait (Pluperfect) Tense
Tense Formation
Common everyday usage patterns
Sequencing of past events
Background information
Hypothetical or reported speech
Interactions with other tenses
Summary
I hope you enjoyed this article on the verb discréditer. Still in a learning mood? Check out another TOTALLY random French verb conjugation!


