Plus-que-parfait (Pluperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb faner
Introduction to the verb faner
The English translation of the French verb faner is “to wilt” or “to fade.” The infinitive form of faner is pronounced as /fa.ne/ with a nasal “e” sound at the end.
Faner comes from the Old French word “fan,” meaning “to fade.” It can also be traced back to the Latin word “fanum,” which means “temple.” In everyday French, faner is commonly used to describe the wilting or fading of plants, flowers, or other organic matter. It can also be used figuratively to describe a person’s appearance or energy.
Examples of faner in the Plus-que-parfait tense:
- J’avais fané les fleurs avant que mes invités arrivent. (I had wilted the flowers before my guests arrived.)
- Tu avais fané tes cheveux en les exposant au soleil toute la journée. (You had faded your hair by exposing it to the sun all day.)
- Ils avaient fané leurs espoirs de gagner le match après la blessure de leur meilleur joueur. (They had wilted their hopes of winning the game after their best player got injured.)
Table of the Plus-que-parfait (Pluperfect) Tense Conjugation of faner
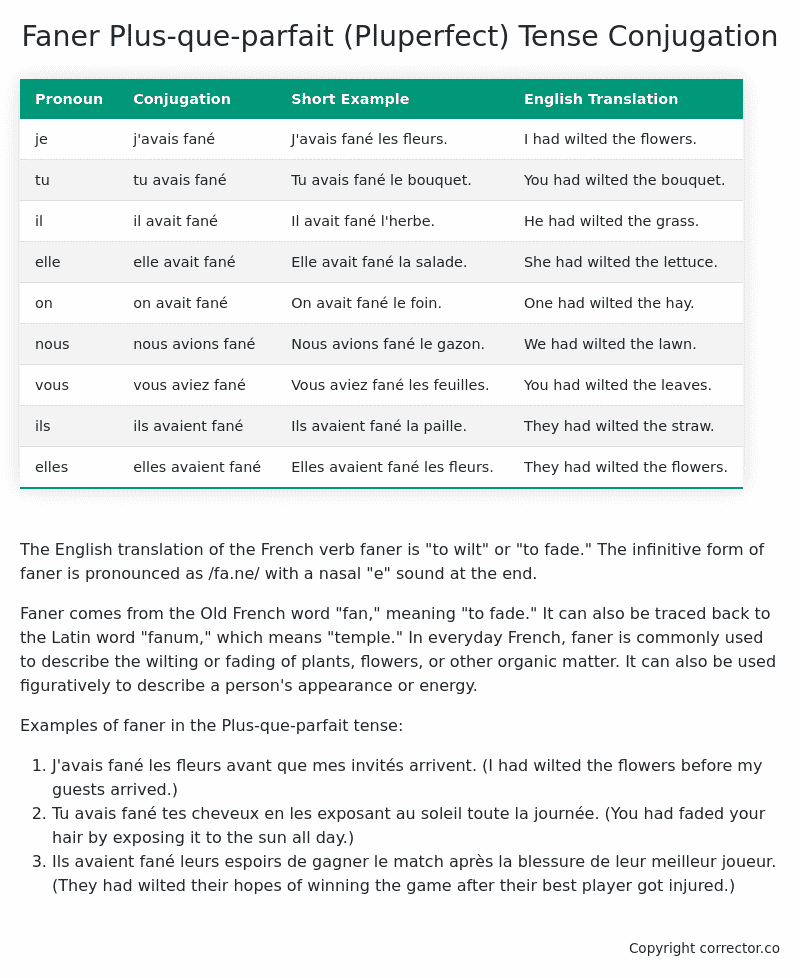
| Pronoun | Conjugation | Short Example | English Translation |
|---|---|---|---|
| je | j’avais fané | J’avais fané les fleurs. | I had wilted the flowers. |
| tu | tu avais fané | Tu avais fané le bouquet. | You had wilted the bouquet. |
| il | il avait fané | Il avait fané l’herbe. | He had wilted the grass. |
| elle | elle avait fané | Elle avait fané la salade. | She had wilted the lettuce. |
| on | on avait fané | On avait fané le foin. | One had wilted the hay. |
| nous | nous avions fané | Nous avions fané le gazon. | We had wilted the lawn. |
| vous | vous aviez fané | Vous aviez fané les feuilles. | You had wilted the leaves. |
| ils | ils avaient fané | Ils avaient fané la paille. | They had wilted the straw. |
| elles | elles avaient fané | Elles avaient fané les fleurs. | They had wilted the flowers. |
Other Conjugations for Faner.
Le Present (Present Tense) Conjugation of the French Verb faner
Imparfait (Imperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb faner
Passé Simple (Simple Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb faner
Passé Composé (Present Perfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb faner
Futur Simple (Simple Future) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb faner
Futur Proche (Near Future) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb faner
Plus-que-parfait (Pluperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb faner (this article)
Passé Antérieur (Past Anterior) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb faner
Futur Antérieur (Future Anterior) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb faner
Subjonctif Présent (Subjunctive Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb faner
Subjonctif Passé (Subjunctive Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb faner
Subjonctif Imparfait (Subjunctive Imperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb faner
Subjonctif Plus-que-parfait (Subjunctive Pluperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb faner
Conditionnel Présent (Conditional Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb faner
Conditionnel Passé (Conditional Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb faner
L’impératif Présent (Imperative Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb faner
L’infinitif Présent (Infinitive Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb faner
Struggling with French verbs or the language in general? Why not use our free French Grammar Checker – no registration required!
Get a FREE Download Study Sheet of this Conjugation 🔥
Simply right click the image below, click “save image” and get your free reference for the faner Plus-que-parfait tense conjugation!
Faner – About the French Plus-que-parfait (Pluperfect) Tense
Tense Formation
Common everyday usage patterns
Sequencing of past events
Background information
Hypothetical or reported speech
Interactions with other tenses
Summary
I hope you enjoyed this article on the verb faner. Still in a learning mood? Check out another TOTALLY random French verb conjugation!


