Plus-que-parfait (Pluperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb maltraiter
Introduction to the verb maltraiter
The English translation of the French verb maltraiter is “to mistreat” or “to abuse.” The infinitive form, maltraiter, is pronounced “mahl-tray-tay.”
The word maltraiter comes from the combination of the prefix “mal” meaning “bad” and the verb “traiter” meaning “to treat.” It originated in Old French and has been used in the French language since the 12th century.
In everyday French, maltraiter is most often used in the Plus-que-parfait tense, which corresponds to the past perfect tense in English. This tense is used to describe an action that was completed before another action in the past.
Example 1: J’avais maltraité mon chat avant de comprendre que c’était cruel.
Translation: I had mistreated my cat before I realized it was cruel.
Example 2: Il avait maltraité ses enfants avant de se rendre compte de l’impact de ses actions.
Translation: He had abused his children before realizing the impact of his actions.
Example 3: Nous avions maltraité les animaux sans même nous en rendre compte.
Translation: We had mistreated the animals without even realizing it.
In all of these examples, the action of maltraiter (mistreating/abusing) occurred before another action in the past (realizing, understanding, noticing).
Table of the Plus-que-parfait (Pluperfect) Tense Conjugation of maltraiter
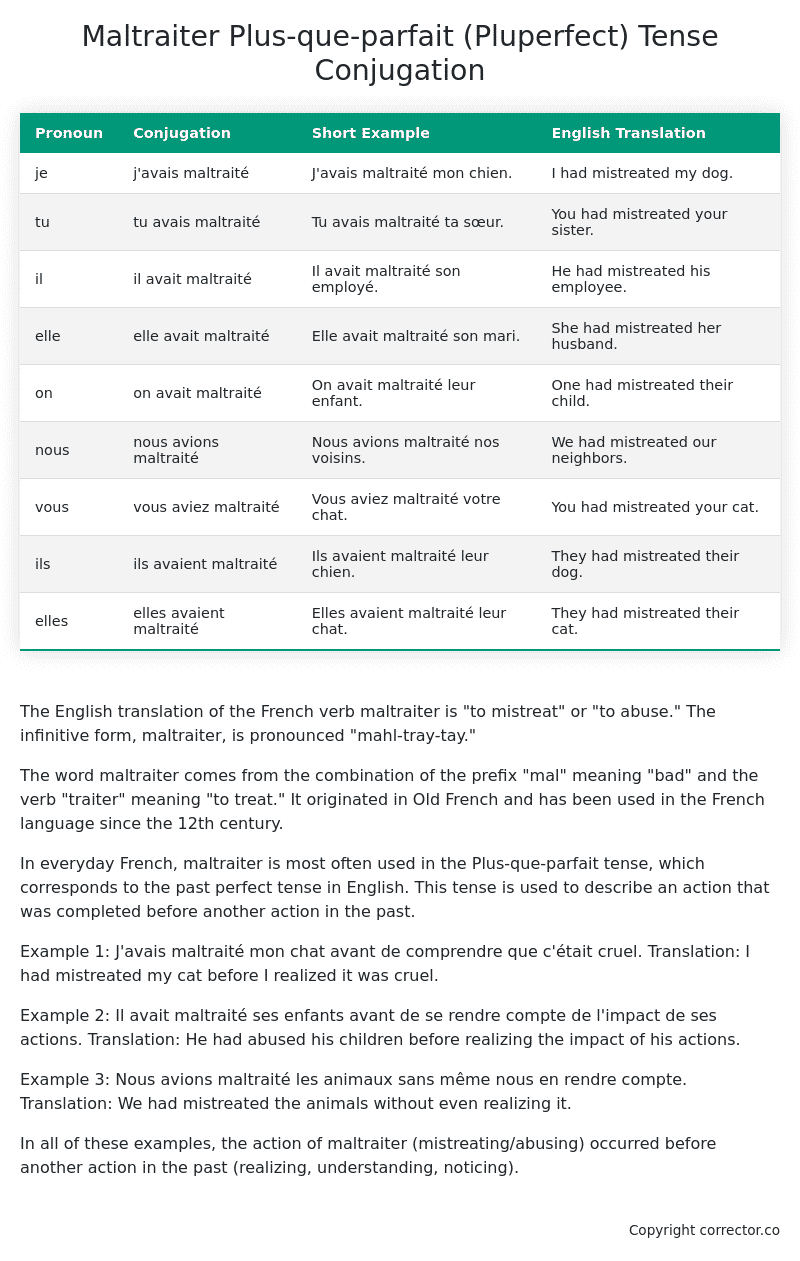
| Pronoun | Conjugation | Short Example | English Translation |
|---|---|---|---|
| je | j’avais maltraité | J’avais maltraité mon chien. | I had mistreated my dog. |
| tu | tu avais maltraité | Tu avais maltraité ta sœur. | You had mistreated your sister. |
| il | il avait maltraité | Il avait maltraité son employé. | He had mistreated his employee. |
| elle | elle avait maltraité | Elle avait maltraité son mari. | She had mistreated her husband. |
| on | on avait maltraité | On avait maltraité leur enfant. | One had mistreated their child. |
| nous | nous avions maltraité | Nous avions maltraité nos voisins. | We had mistreated our neighbors. |
| vous | vous aviez maltraité | Vous aviez maltraité votre chat. | You had mistreated your cat. |
| ils | ils avaient maltraité | Ils avaient maltraité leur chien. | They had mistreated their dog. |
| elles | elles avaient maltraité | Elles avaient maltraité leur chat. | They had mistreated their cat. |
Other Conjugations for Maltraiter.
Le Present (Present Tense) Conjugation of the French Verb maltraiter
Imparfait (Imperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb maltraiter
Passé Simple (Simple Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb maltraiter
Passé Composé (Present Perfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb maltraiter
Futur Simple (Simple Future) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb maltraiter
Futur Proche (Near Future) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb maltraiter
Plus-que-parfait (Pluperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb maltraiter (this article)
Passé Antérieur (Past Anterior) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb maltraiter
Futur Antérieur (Future Anterior) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb maltraiter
Subjonctif Présent (Subjunctive Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb maltraiter
Subjonctif Passé (Subjunctive Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb maltraiter
Subjonctif Imparfait (Subjunctive Imperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb maltraiter
Subjonctif Plus-que-parfait (Subjunctive Pluperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb maltraiter
Conditionnel Présent (Conditional Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb maltraiter
Conditionnel Passé (Conditional Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb maltraiter
L’impératif Présent (Imperative Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb maltraiter
L’infinitif Présent (Infinitive Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb maltraiter
Struggling with French verbs or the language in general? Why not use our free French Grammar Checker – no registration required!
Get a FREE Download Study Sheet of this Conjugation 🔥
Simply right click the image below, click “save image” and get your free reference for the maltraiter Plus-que-parfait tense conjugation!
Maltraiter – About the French Plus-que-parfait (Pluperfect) Tense
Tense Formation
Common everyday usage patterns
Sequencing of past events
Background information
Hypothetical or reported speech
Interactions with other tenses
Summary
I hope you enjoyed this article on the verb maltraiter. Still in a learning mood? Check out another TOTALLY random French verb conjugation!


