Plus-que-parfait (Pluperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb préexister
Introduction to the verb préexister
The English translation of the French verb préexister is “to preexist.” The infinitive form is pronounced “pray-ehg-zee-stay.”
Préexister comes from the Latin term praexistere, which means “to exist beforehand.” It is most often used in everyday French in the Plus-que-parfait tense, which corresponds to the English past perfect tense. This tense is used to describe an action that occurred before another past action or event.
Examples:
-
Avant de rencontrer son mari, elle avait préexisté seule pendant plusieurs années. (Before meeting her husband, she had existed alone for several years.)
-
Les anciennes traditions avaient préexisté avant l’arrivée des colons européens. (The old traditions had preexisted before the arrival of the European colonists.)
-
Avant même que l’univers ne soit créé, Dieu avait préexisté depuis toujours. (Even before the universe was created, God had preexisted for eternity.)
Table of the Plus-que-parfait (Pluperfect) Tense Conjugation of préexister
| Pronoun | Conjugation | Short Example | English Translation |
|---|---|---|---|
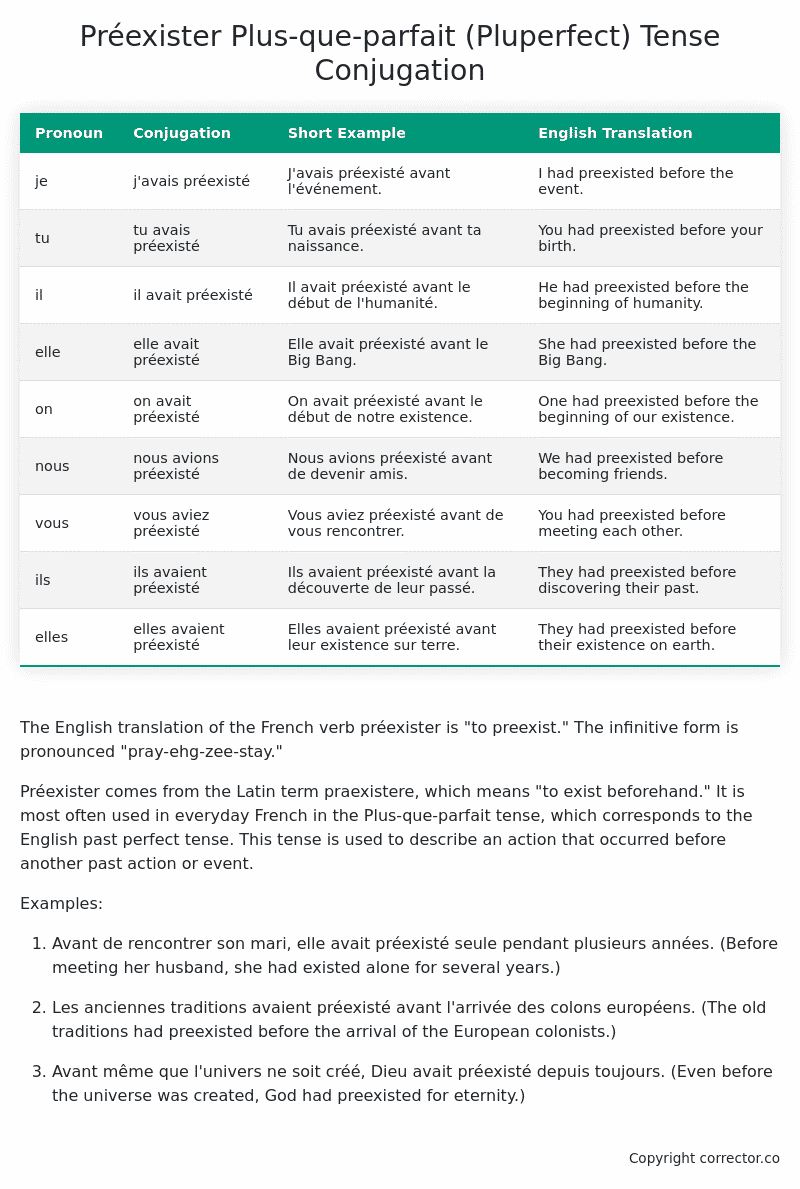
| je | j’avais préexisté | J’avais préexisté avant l’événement. | I had preexisted before the event. |
| tu | tu avais préexisté | Tu avais préexisté avant ta naissance. | You had preexisted before your birth. |
| il | il avait préexisté | Il avait préexisté avant le début de l’humanité. | He had preexisted before the beginning of humanity. |
| elle | elle avait préexisté | Elle avait préexisté avant le Big Bang. | She had preexisted before the Big Bang. |
| on | on avait préexisté | On avait préexisté avant le début de notre existence. | One had preexisted before the beginning of our existence. |
| nous | nous avions préexisté | Nous avions préexisté avant de devenir amis. | We had preexisted before becoming friends. |
| vous | vous aviez préexisté | Vous aviez préexisté avant de vous rencontrer. | You had preexisted before meeting each other. |
| ils | ils avaient préexisté | Ils avaient préexisté avant la découverte de leur passé. | They had preexisted before discovering their past. |
| elles | elles avaient préexisté | Elles avaient préexisté avant leur existence sur terre. | They had preexisted before their existence on earth. |
Other Conjugations for Préexister.
Le Present (Present Tense) Conjugation of the French Verb préexister
Imparfait (Imperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb préexister
Passé Simple (Simple Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb préexister
Passé Composé (Present Perfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb préexister
Futur Simple (Simple Future) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb préexister
Futur Proche (Near Future) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb préexister
Plus-que-parfait (Pluperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb préexister (this article)
Passé Antérieur (Past Anterior) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb préexister
Futur Antérieur (Future Anterior) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb préexister
Subjonctif Présent (Subjunctive Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb préexister
Subjonctif Passé (Subjunctive Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb préexister
Subjonctif Imparfait (Subjunctive Imperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb préexister
Subjonctif Plus-que-parfait (Subjunctive Pluperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb préexister
Conditionnel Présent (Conditional Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb préexister
Conditionnel Passé (Conditional Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb préexister
L’impératif Présent (Imperative Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb préexister
L’infinitif Présent (Infinitive Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb préexister
Struggling with French verbs or the language in general? Why not use our free French Grammar Checker – no registration required!
Get a FREE Download Study Sheet of this Conjugation 🔥
Simply right click the image below, click “save image” and get your free reference for the préexister Plus-que-parfait tense conjugation!
Préexister – About the French Plus-que-parfait (Pluperfect) Tense
Tense Formation
Common everyday usage patterns
Sequencing of past events
Background information
Hypothetical or reported speech
Interactions with other tenses
Summary
I hope you enjoyed this article on the verb préexister. Still in a learning mood? Check out another TOTALLY random French verb conjugation!


