Plus-que-parfait (Pluperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb rançonner
Introduction to the verb rançonner
The English translation of the French verb rançonner is “to ransom” or “to extort”. It is pronounced as “rahn-soh-nay”.
The language origin of rançonner can be traced back to the Old French word “ranson” which means “ransom” or “payment”. It comes from the Latin word “redemptionem” which also means “ransom”. In modern French, rançonner is most often used in the context of extortion or demanding payment from someone in exchange for their release or protection.
In everyday French, rançonner is commonly used in the Plus-que-parfait tense, which is the past perfect tense. This tense is used to describe an action that was completed before another past action. Here are three examples of its usage in this tense:
- J’avais été rançonné par les bandits avant que la police n’arrive. (I had been extorted by the bandits before the police arrived.)
- Il avait été rançonné par son propre frère pour accéder à l’héritage familial. (He had been extorted by his own brother to access the family inheritance.)
- Les habitants du village avaient été rançonnés par le seigneur local pendant des années avant de se révolter. (The villagers had been extorted by the local lord for years before rebelling.)
Table of the Plus-que-parfait (Pluperfect) Tense Conjugation of rançonner
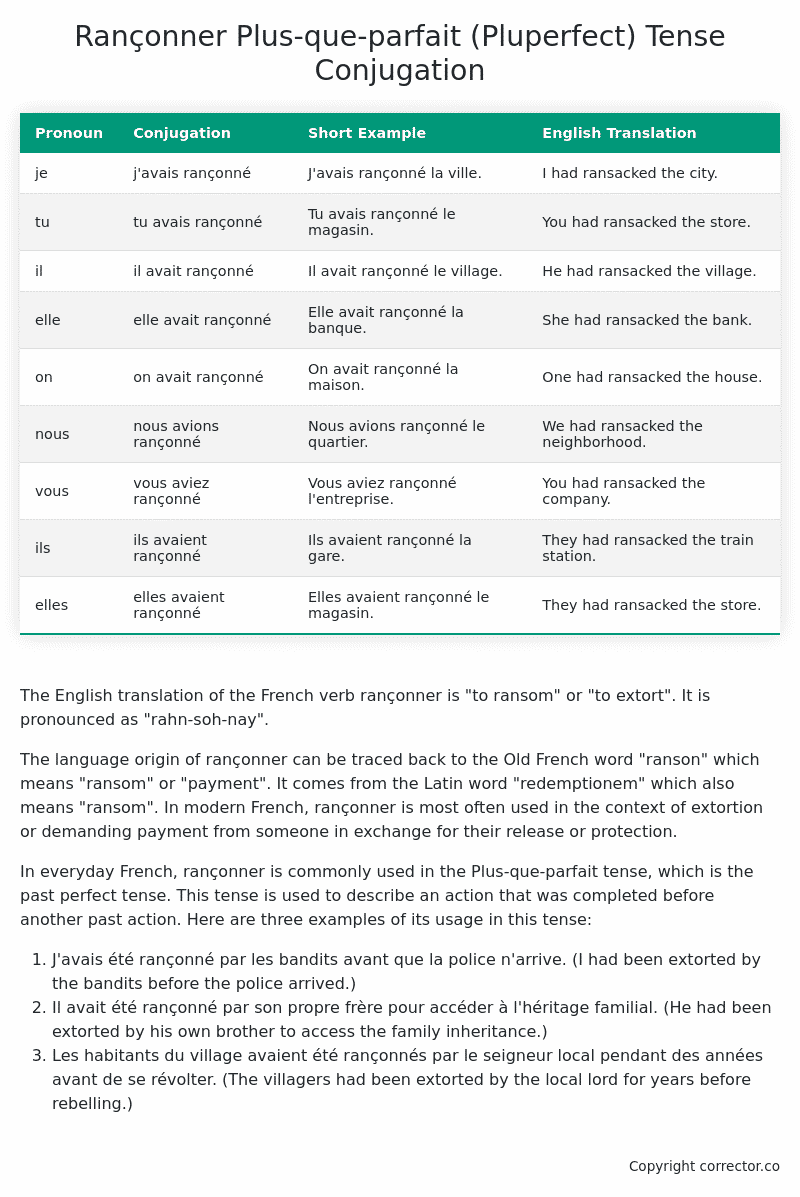
| Pronoun | Conjugation | Short Example | English Translation |
|---|---|---|---|
| je | j’avais rançonné | J’avais rançonné la ville. | I had ransacked the city. |
| tu | tu avais rançonné | Tu avais rançonné le magasin. | You had ransacked the store. |
| il | il avait rançonné | Il avait rançonné le village. | He had ransacked the village. |
| elle | elle avait rançonné | Elle avait rançonné la banque. | She had ransacked the bank. |
| on | on avait rançonné | On avait rançonné la maison. | One had ransacked the house. |
| nous | nous avions rançonné | Nous avions rançonné le quartier. | We had ransacked the neighborhood. |
| vous | vous aviez rançonné | Vous aviez rançonné l’entreprise. | You had ransacked the company. |
| ils | ils avaient rançonné | Ils avaient rançonné la gare. | They had ransacked the train station. |
| elles | elles avaient rançonné | Elles avaient rançonné le magasin. | They had ransacked the store. |
Other Conjugations for Rançonner.
Le Present (Present Tense) Conjugation of the French Verb rançonner
Imparfait (Imperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb rançonner
Passé Simple (Simple Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb rançonner
Passé Composé (Present Perfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb rançonner
Futur Simple (Simple Future) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb rançonner
Futur Proche (Near Future) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb rançonner
Plus-que-parfait (Pluperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb rançonner (this article)
Passé Antérieur (Past Anterior) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb rançonner
Futur Antérieur (Future Anterior) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb rançonner
Subjonctif Présent (Subjunctive Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb rançonner
Subjonctif Passé (Subjunctive Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb rançonner
Subjonctif Imparfait (Subjunctive Imperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb rançonner
Subjonctif Plus-que-parfait (Subjunctive Pluperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb rançonner
Conditionnel Présent (Conditional Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb rançonner
Conditionnel Passé (Conditional Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb rançonner
L’impératif Présent (Imperative Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb rançonner
L’infinitif Présent (Infinitive Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb rançonner
Struggling with French verbs or the language in general? Why not use our free French Grammar Checker – no registration required!
Get a FREE Download Study Sheet of this Conjugation 🔥
Simply right click the image below, click “save image” and get your free reference for the rançonner Plus-que-parfait tense conjugation!
Rançonner – About the French Plus-que-parfait (Pluperfect) Tense
Tense Formation
Common everyday usage patterns
Sequencing of past events
Background information
Hypothetical or reported speech
Interactions with other tenses
Summary
I hope you enjoyed this article on the verb rançonner. Still in a learning mood? Check out another TOTALLY random French verb conjugation!


