Plus-que-parfait (Pluperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb rapiéceter
Introduction to the verb rapiéceter
The English translation of the French verb rapiéceter is “to patch up” or “to mend.” It is pronounced as “ra-pee-se-tay.”
The word rapiéceter comes from the French word “pièce,” meaning “piece,” and the verb “coudre,” meaning “to sew.” It is most often used in everyday French in the Plus-que-parfait tense, which is the past perfect tense in English.
The Plus-que-parfait tense is used to talk about an action that was completed before another action in the past. It is formed with the auxiliary verb “avoir” or “être” in the imperfect tense, followed by the past participle of the main verb.
Examples of rapiéceter in the Plus-que-parfait tense are:
- J’avais rapiéceté mon pantalon avant de partir en vacances. (I had patched up my pants before going on vacation.)
- Elle était déjà partie lorsque j’ai rapiéceté son pull. (She had already left when I patched up her sweater.)
- Nous avions rapiéceté le toit de la maison avant l’arrivée de la pluie. (We had patched up the roof of the house before the rain came.)
In all of these examples, the action of patching up or mending happened before another action in the past. In English, the Plus-que-parfait tense is equivalent to the past perfect tense, which also expresses an action that was completed before another action in the past.
Table of the Plus-que-parfait (Pluperfect) Tense Conjugation of rapiéceter
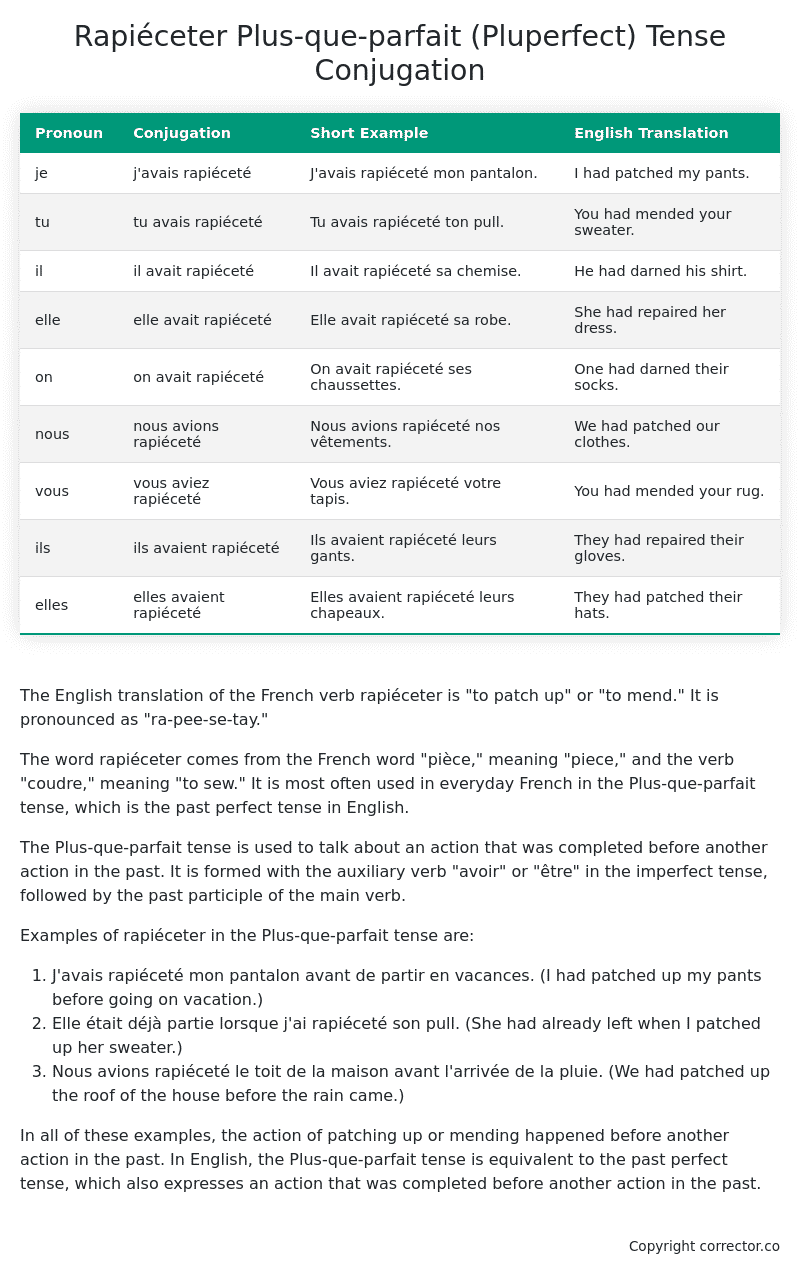
| Pronoun | Conjugation | Short Example | English Translation |
|---|---|---|---|
| je | j’avais rapiéceté | J’avais rapiéceté mon pantalon. | I had patched my pants. |
| tu | tu avais rapiéceté | Tu avais rapiéceté ton pull. | You had mended your sweater. |
| il | il avait rapiéceté | Il avait rapiéceté sa chemise. | He had darned his shirt. |
| elle | elle avait rapiéceté | Elle avait rapiéceté sa robe. | She had repaired her dress. |
| on | on avait rapiéceté | On avait rapiéceté ses chaussettes. | One had darned their socks. |
| nous | nous avions rapiéceté | Nous avions rapiéceté nos vêtements. | We had patched our clothes. |
| vous | vous aviez rapiéceté | Vous aviez rapiéceté votre tapis. | You had mended your rug. |
| ils | ils avaient rapiéceté | Ils avaient rapiéceté leurs gants. | They had repaired their gloves. |
| elles | elles avaient rapiéceté | Elles avaient rapiéceté leurs chapeaux. | They had patched their hats. |
Other Conjugations for Rapiéceter.
Le Present (Present Tense) Conjugation of the French Verb rapiéceter
Imparfait (Imperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb rapiéceter
Passé Simple (Simple Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb rapiéceter
Passé Composé (Present Perfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb rapiéceter
Futur Simple (Simple Future) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb rapiéceter
Futur Proche (Near Future) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb rapiéceter
Plus-que-parfait (Pluperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb rapiéceter (this article)
Passé Antérieur (Past Anterior) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb rapiéceter
Futur Antérieur (Future Anterior) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb rapiéceter
Subjonctif Présent (Subjunctive Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb rapiéceter
Subjonctif Passé (Subjunctive Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb rapiéceter
Subjonctif Imparfait (Subjunctive Imperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb rapiéceter
Subjonctif Plus-que-parfait (Subjunctive Pluperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb rapiéceter
Conditionnel Présent (Conditional Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb rapiéceter
Conditionnel Passé (Conditional Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb rapiéceter
L’impératif Présent (Imperative Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb rapiéceter
L’infinitif Présent (Infinitive Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb rapiéceter
Struggling with French verbs or the language in general? Why not use our free French Grammar Checker – no registration required!
Get a FREE Download Study Sheet of this Conjugation 🔥
Simply right click the image below, click “save image” and get your free reference for the rapiéceter Plus-que-parfait tense conjugation!
Rapiéceter – About the French Plus-que-parfait (Pluperfect) Tense
Tense Formation
Common everyday usage patterns
Sequencing of past events
Background information
Hypothetical or reported speech
Interactions with other tenses
Summary
I hope you enjoyed this article on the verb rapiéceter. Still in a learning mood? Check out another TOTALLY random French verb conjugation!


