Subjonctif Imparfait (Subjunctive Imperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb alléguer
Introduction to the verb alléguer
The English translation of the French verb alléguer is “to allege” or “to claim.” It is pronounced as “ah-leh-guh-ray” in its infinitive form.
The language origin of alléguer comes from the Latin word “allēgāre,” meaning “to bring forward as evidence.” In everyday French, alléguer is most often used in the Subjonctif Imparfait tense, which is a verb tense used to express a hypothetical or uncertain action in the past.
Three simple examples of its usage in the Subjonctif Imparfait tense are:
- J’aurais aimé que tu alléguasses ta présence à la réunion. (I wish you had alleged your presence at the meeting.)
- Il était important que nous alléguassions des preuves solides pour notre défense. (It was important that we alleged solid evidence for our defense.)
- Si elles avaient allégué leur maladie, elles auraient été excusées pour leur absence. (If they had alleged their illness, they would have been excused for their absence.)
Table of the Subjonctif Imparfait (Subjunctive Imperfect) Tense Conjugation of alléguer
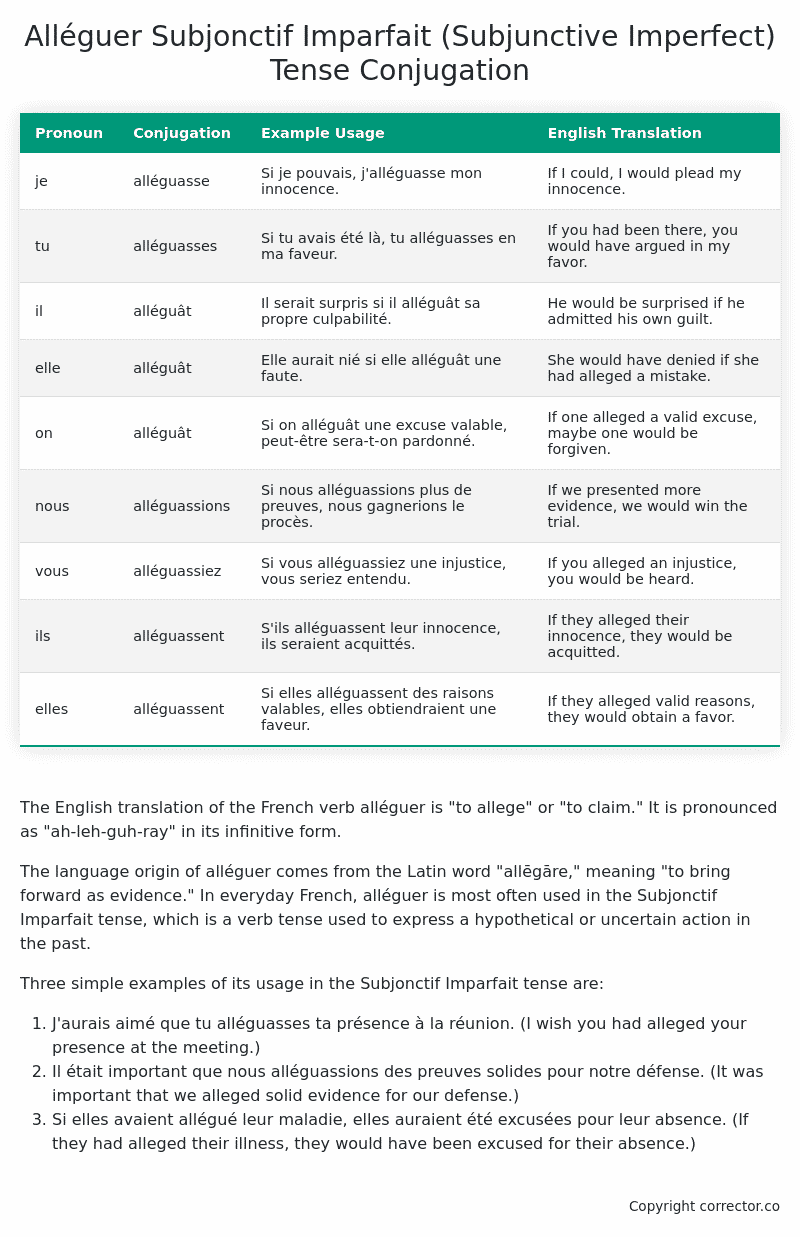
| Pronoun | Conjugation | Example Usage | English Translation |
|---|---|---|---|
| je | alléguasse | Si je pouvais, j’alléguasse mon innocence. | If I could, I would plead my innocence. |
| tu | alléguasses | Si tu avais été là, tu alléguasses en ma faveur. | If you had been there, you would have argued in my favor. |
| il | alléguât | Il serait surpris si il alléguât sa propre culpabilité. | He would be surprised if he admitted his own guilt. |
| elle | alléguât | Elle aurait nié si elle alléguât une faute. | She would have denied if she had alleged a mistake. |
| on | alléguât | Si on alléguât une excuse valable, peut-être sera-t-on pardonné. | If one alleged a valid excuse, maybe one would be forgiven. |
| nous | alléguassions | Si nous alléguassions plus de preuves, nous gagnerions le procès. | If we presented more evidence, we would win the trial. |
| vous | alléguassiez | Si vous alléguassiez une injustice, vous seriez entendu. | If you alleged an injustice, you would be heard. |
| ils | alléguassent | S’ils alléguassent leur innocence, ils seraient acquittés. | If they alleged their innocence, they would be acquitted. |
| elles | alléguassent | Si elles alléguassent des raisons valables, elles obtiendraient une faveur. | If they alleged valid reasons, they would obtain a favor. |
Other Conjugations for Alléguer.
Le Present (Present Tense) Conjugation of the French Verb alléguer
Imparfait (Imperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb alléguer
Passé Simple (Simple Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb alléguer
Passé Composé (Present Perfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb alléguer
Futur Simple (Simple Future) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb alléguer
Futur Proche (Near Future) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb alléguer
Plus-que-parfait (Pluperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb alléguer
Passé Antérieur (Past Anterior) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb alléguer
Futur Antérieur (Future Anterior) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb alléguer
Subjonctif Présent (Subjunctive Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb alléguer
Subjonctif Passé (Subjunctive Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb alléguer
Subjonctif Imparfait (Subjunctive Imperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb alléguer (this article)
Subjonctif Plus-que-parfait (Subjunctive Pluperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb alléguer
Conditionnel Présent (Conditional Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb alléguer
Conditionnel Passé (Conditional Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb alléguer
L’impératif Présent (Imperative Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb alléguer
L’infinitif Présent (Infinitive Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb alléguer
Struggling with French verbs or the language in general? Why not use our free French Grammar Checker – no registration required!
Get a FREE Download Study Sheet of this Conjugation 🔥
Simply right click the image below, click “save image” and get your free reference for the alléguer Subjonctif Imparfait tense conjugation!
Alléguer – About the French Subjonctif Imparfait (Subjunctive Imperfect) Tense
Formation
Common Everyday Usage Patterns
Interactions with Other Tenses
Subjonctif Présent
Indicatif Passé Composé
Conditional
Conditional Perfect
Summary
I hope you enjoyed this article on the verb alléguer. Still in a learning mood? Check out another TOTALLY random French verb conjugation!


