Subjonctif Imparfait (Subjunctive Imperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb corner
Introduction to the verb corner
The English translation of the French verb corner is “to corner.” It is pronounced “kohrn-ay.”
The word “corner” has its origin in Old French, derived from the Latin word “cornu,” meaning “horn.” It was initially used to refer to a sharp angle or point, and the verb “corner” was used to describe the act of placing something in a corner or trapping someone in a corner. In everyday French, the verb corner is often used in the Subjonctif Imparfait (imperfect subjunctive) tense, which is used to express a hypothetical or uncertain action in the past.
Three simple examples of the usage of corner in the Subjonctif Imparfait tense are:
- Je souhaitais que tu corners la conversation avant qu’il ne se fâche. (I wished that you would corner the conversation before he got angry.)
- Il était important que nous corners le marché avant que nos concurrents ne le fassent. (It was important that we cornered the market before our competitors did.)
- Les policiers ont décidé d’arrêter le suspect avant qu’il ne corners l’entrée de la banque. (The police decided to arrest the suspect before he cornered the entrance of the bank.)
Table of the Subjonctif Imparfait (Subjunctive Imperfect) Tense Conjugation of corner
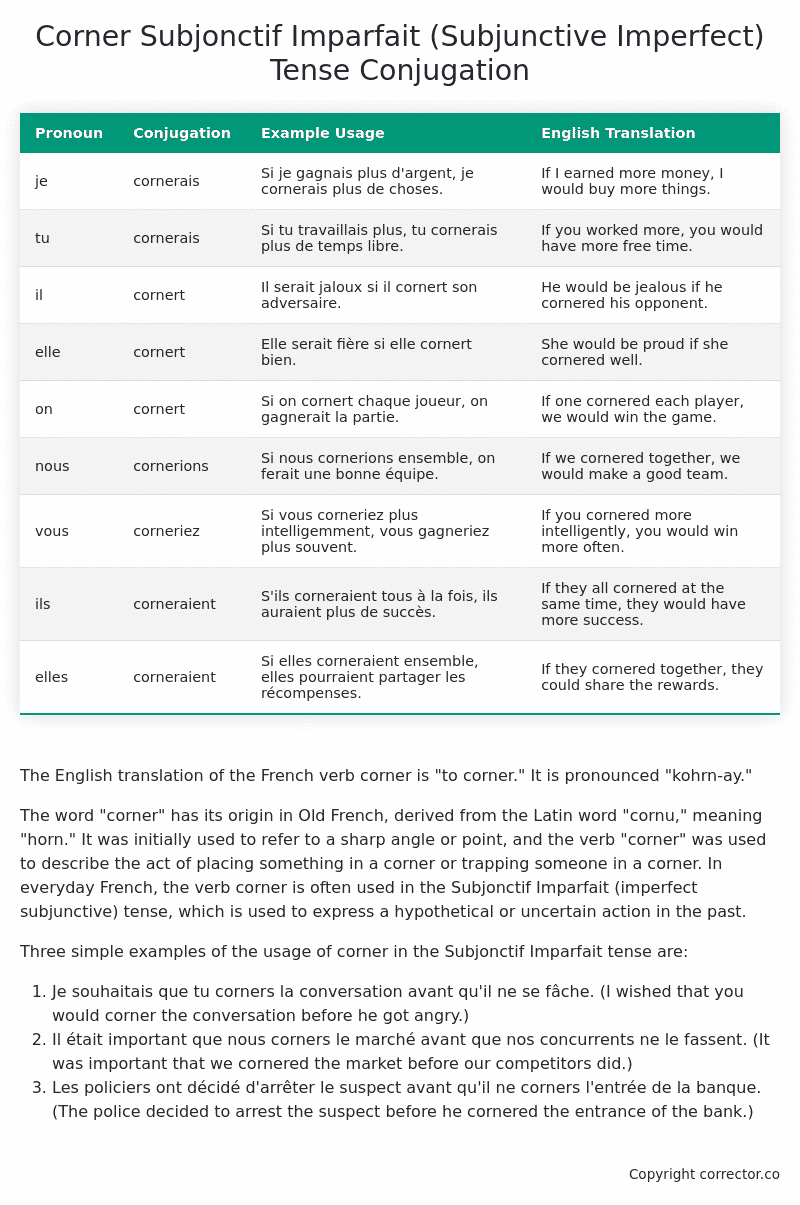
| Pronoun | Conjugation | Example Usage | English Translation |
|---|---|---|---|
| je | cornerais | Si je gagnais plus d’argent, je cornerais plus de choses. | If I earned more money, I would buy more things. |
| tu | cornerais | Si tu travaillais plus, tu cornerais plus de temps libre. | If you worked more, you would have more free time. |
| il | cornert | Il serait jaloux si il cornert son adversaire. | He would be jealous if he cornered his opponent. |
| elle | cornert | Elle serait fière si elle cornert bien. | She would be proud if she cornered well. |
| on | cornert | Si on cornert chaque joueur, on gagnerait la partie. | If one cornered each player, we would win the game. |
| nous | cornerions | Si nous cornerions ensemble, on ferait une bonne équipe. | If we cornered together, we would make a good team. |
| vous | corneriez | Si vous corneriez plus intelligemment, vous gagneriez plus souvent. | If you cornered more intelligently, you would win more often. |
| ils | corneraient | S’ils corneraient tous à la fois, ils auraient plus de succès. | If they all cornered at the same time, they would have more success. |
| elles | corneraient | Si elles corneraient ensemble, elles pourraient partager les récompenses. | If they cornered together, they could share the rewards. |
Other Conjugations for Corner.
Le Present (Present Tense) Conjugation of the French Verb corner
Imparfait (Imperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb corner
Passé Simple (Simple Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb corner
Passé Composé (Present Perfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb corner
Futur Simple (Simple Future) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb corner
Futur Proche (Near Future) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb corner
Plus-que-parfait (Pluperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb corner
Passé Antérieur (Past Anterior) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb corner
Futur Antérieur (Future Anterior) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb corner
Subjonctif Présent (Subjunctive Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb corner
Subjonctif Passé (Subjunctive Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb corner
Subjonctif Imparfait (Subjunctive Imperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb corner (this article)
Subjonctif Plus-que-parfait (Subjunctive Pluperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb corner
Conditionnel Présent (Conditional Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb corner
Conditionnel Passé (Conditional Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb corner
L’impératif Présent (Imperative Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb corner
L’infinitif Présent (Infinitive Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb corner
Struggling with French verbs or the language in general? Why not use our free French Grammar Checker – no registration required!
Get a FREE Download Study Sheet of this Conjugation 🔥
Simply right click the image below, click “save image” and get your free reference for the corner Subjonctif Imparfait tense conjugation!
Corner – About the French Subjonctif Imparfait (Subjunctive Imperfect) Tense
Formation
Common Everyday Usage Patterns
Interactions with Other Tenses
Subjonctif Présent
Indicatif Passé Composé
Conditional
Conditional Perfect
Summary
I hope you enjoyed this article on the verb corner. Still in a learning mood? Check out another TOTALLY random French verb conjugation!


