Subjonctif Passé (Subjunctive Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb assécher
Introduction to the verb assécher
The English translation of the French verb assécher is “to dry out.” It is pronounced as “ah-seh-shay.”
Assécher comes from the Latin word “siccāre” meaning “to make dry.” It is most often used in everyday French in the Subjonctif Passé tense to express a hypothetical action or event that occurred in the past.
Example 1:
J’aurais aimé que tu aies asséché les vêtements avant de les mettre dans le sèche-linge.
I would have liked you to have dried the clothes before putting them in the dryer.
Example 2:
Elle aurait préféré que nous ayons asséché les draps avant de les étendre sur le fil.
She would have preferred that we had dried the sheets before hanging them on the line.
Example 3:
Je regrette que vous n’ayez pas asséché la vaisselle avant de la ranger.
I regret that you did not dry the dishes before putting them away.
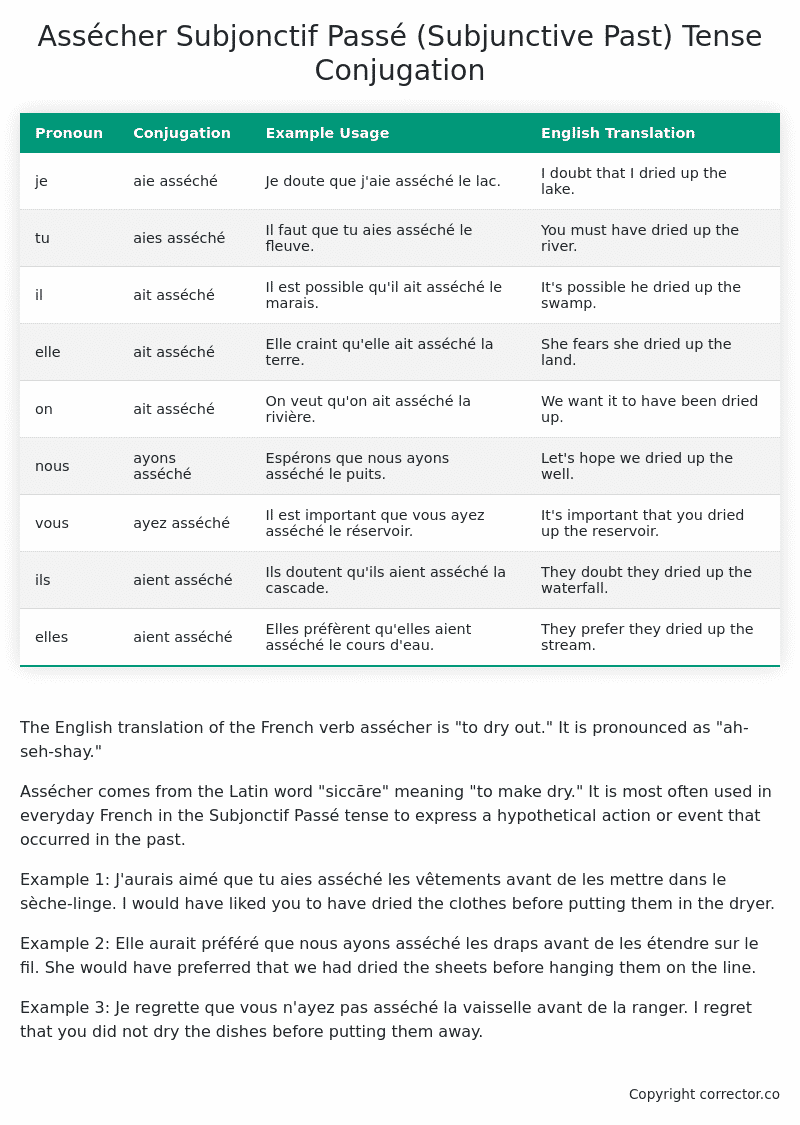
Table of the Subjonctif Passé (Subjunctive Past) Tense Conjugation of assécher
| Pronoun | Conjugation | Example Usage | English Translation |
|---|---|---|---|
| je | aie asséché | Je doute que j’aie asséché le lac. | I doubt that I dried up the lake. |
| tu | aies asséché | Il faut que tu aies asséché le fleuve. | You must have dried up the river. |
| il | ait asséché | Il est possible qu’il ait asséché le marais. | It’s possible he dried up the swamp. |
| elle | ait asséché | Elle craint qu’elle ait asséché la terre. | She fears she dried up the land. |
| on | ait asséché | On veut qu’on ait asséché la rivière. | We want it to have been dried up. |
| nous | ayons asséché | Espérons que nous ayons asséché le puits. | Let’s hope we dried up the well. |
| vous | ayez asséché | Il est important que vous ayez asséché le réservoir. | It’s important that you dried up the reservoir. |
| ils | aient asséché | Ils doutent qu’ils aient asséché la cascade. | They doubt they dried up the waterfall. |
| elles | aient asséché | Elles préfèrent qu’elles aient asséché le cours d’eau. | They prefer they dried up the stream. |
Other Conjugations for Assécher.
Le Present (Present Tense) Conjugation of the French Verb assécher
Imparfait (Imperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb assécher
Passé Simple (Simple Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb assécher
Passé Composé (Present Perfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb assécher
Futur Simple (Simple Future) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb assécher
Futur Proche (Near Future) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb assécher
Plus-que-parfait (Pluperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb assécher
Passé Antérieur (Past Anterior) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb assécher
Futur Antérieur (Future Anterior) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb assécher
Subjonctif Présent (Subjunctive Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb assécher
Subjonctif Passé (Subjunctive Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb assécher (this article)
Subjonctif Imparfait (Subjunctive Imperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb assécher
Subjonctif Plus-que-parfait (Subjunctive Pluperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb assécher
Conditionnel Présent (Conditional Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb assécher
Conditionnel Passé (Conditional Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb assécher
L’impératif Présent (Imperative Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb assécher
L’infinitif Présent (Infinitive Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb assécher
Struggling with French verbs or the language in general? Why not use our free French Grammar Checker – no registration required!
Get a FREE Download Study Sheet of this Conjugation 🔥
Simply right click the image below, click “save image” and get your free reference for the assécher Subjonctif Passé tense conjugation!
Assécher – About the French Subjonctif Passé (Subjunctive Past) Tense
Formation of the Subjonctif Passé
Everyday Usage Patterns
Interactions with Other Tenses
Present tense
Future tense
Conditional
Summary
I hope you enjoyed this article on the verb assécher. Still in a learning mood? Check out another TOTALLY random French verb conjugation!


