L’impératif Présent (Imperative Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb aviser
Introduction to the verb aviser
The English translation of the French verb aviser is “to advise” or “to inform.” It is pronounced “ah-vee-zay.”
The word aviser comes from the Latin word “advisare” meaning “to look at” or “to consider.” In everyday French, aviser is most often used in the L’impératif Présent tense, which is the imperative form used to give commands or instructions.
Three simple examples of aviser in the L’impératif Présent tense with their English translations are:
- “Avisez-moi si vous avez besoin d’aide.” (Advise me if you need help.)
- “Avisez vos collègues du changement de programme.” (Inform your colleagues of the change in schedule.)
- “Avisez-moi dès que vous avez des nouvelles.” (Let me know as soon as you have news.)
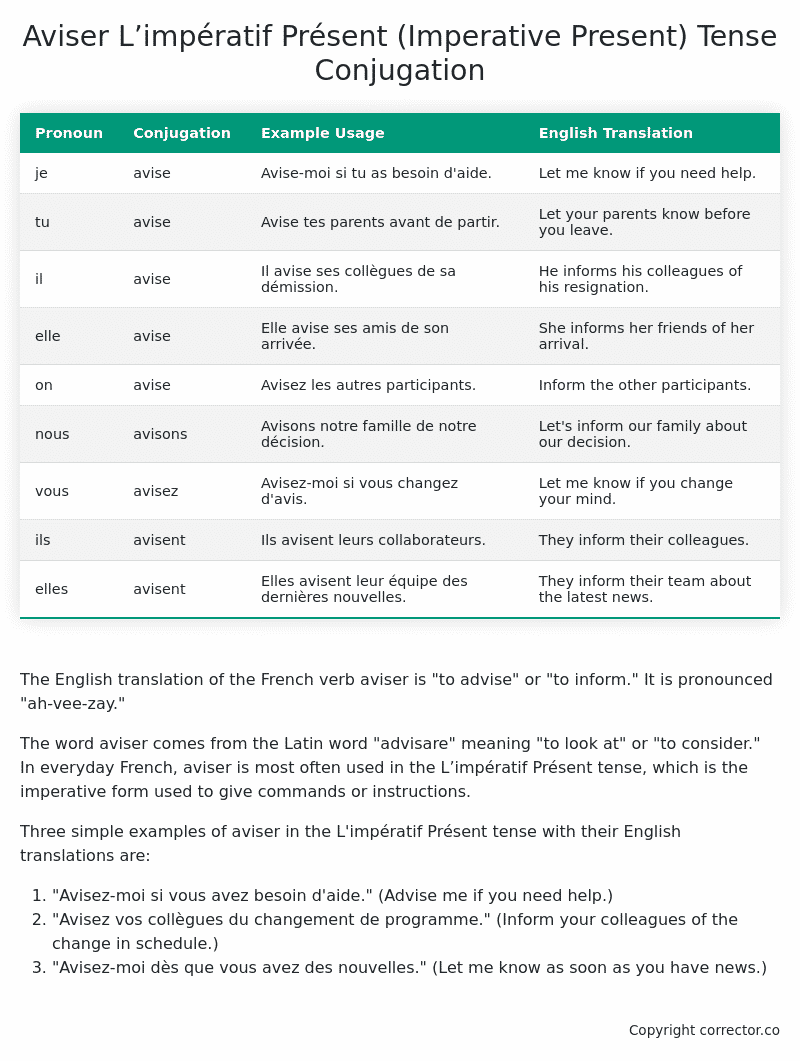
Table of the L’impératif Présent (Imperative Present) Tense Conjugation of aviser
| Pronoun | Conjugation | Example Usage | English Translation |
|---|---|---|---|
| je | avise | Avise-moi si tu as besoin d’aide. | Let me know if you need help. |
| tu | avise | Avise tes parents avant de partir. | Let your parents know before you leave. |
| il | avise | Il avise ses collègues de sa démission. | He informs his colleagues of his resignation. |
| elle | avise | Elle avise ses amis de son arrivée. | She informs her friends of her arrival. |
| on | avise | Avisez les autres participants. | Inform the other participants. |
| nous | avisons | Avisons notre famille de notre décision. | Let’s inform our family about our decision. |
| vous | avisez | Avisez-moi si vous changez d’avis. | Let me know if you change your mind. |
| ils | avisent | Ils avisent leurs collaborateurs. | They inform their colleagues. |
| elles | avisent | Elles avisent leur équipe des dernières nouvelles. | They inform their team about the latest news. |
Other Conjugations for Aviser.
Le Present (Present Tense) Conjugation of the French Verb aviser
Imparfait (Imperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb aviser
Passé Simple (Simple Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb aviser
Passé Composé (Present Perfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb aviser
Futur Simple (Simple Future) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb aviser
Futur Proche (Near Future) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb aviser
Plus-que-parfait (Pluperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb aviser
Passé Antérieur (Past Anterior) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb aviser
Futur Antérieur (Future Anterior) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb aviser
Subjonctif Présent (Subjunctive Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb aviser
Subjonctif Passé (Subjunctive Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb aviser
Subjonctif Imparfait (Subjunctive Imperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb aviser
Subjonctif Plus-que-parfait (Subjunctive Pluperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb aviser
Conditionnel Présent (Conditional Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb aviser
Conditionnel Passé (Conditional Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb aviser
L’impératif Présent (Imperative Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb aviser (this article)
L’infinitif Présent (Infinitive Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb aviser
Struggling with French verbs or the language in general? Why not use our free French Grammar Checker – no registration required!
Get a FREE Download Study Sheet of this Conjugation 🔥
Simply right click the image below, click “save image” and get your free reference for the aviser L’impératif Présent tense conjugation!
Aviser – About the French L’impératif Présent (Imperative Present) Tense
Usage
Giving commands
Making requests
Offering advice
Expressing desires
Conjugation Formation
Interactions with other tenses
Want More?
I hope you enjoyed this article on the verb aviser. Still in a learning mood? Check out another TOTALLY random French verb conjugation!


