L’infinitif Présent (Infinitive Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb bruler
Introduction to the verb bruler
The English translation of the French verb bruler is “to burn.” It is pronounced as “buh-ler” in the infinitive form.
The word bruler comes from the Latin word “bruciare” which means “to burn.” It has been used in French since the 12th century.
In everyday French, bruler is most often used in the l’infinitif présent tense to describe actions or processes that are ongoing or continuous. Here are three simple examples of its usage:
-
Je vais bruler les branches dans le jardin. (I am going to burn the branches in the garden.)
-
Il adore bruler des bougies pour créer une ambiance chaleureuse. (He loves to burn candles to create a cozy atmosphere.)
-
Nous ne devons pas bruler nos déchets, c’est mauvais pour l’environnement. (We must not burn our waste, it’s bad for the environment.)
Table of the L’infinitif Présent (Infinitive Present) Tense Conjugation of bruler
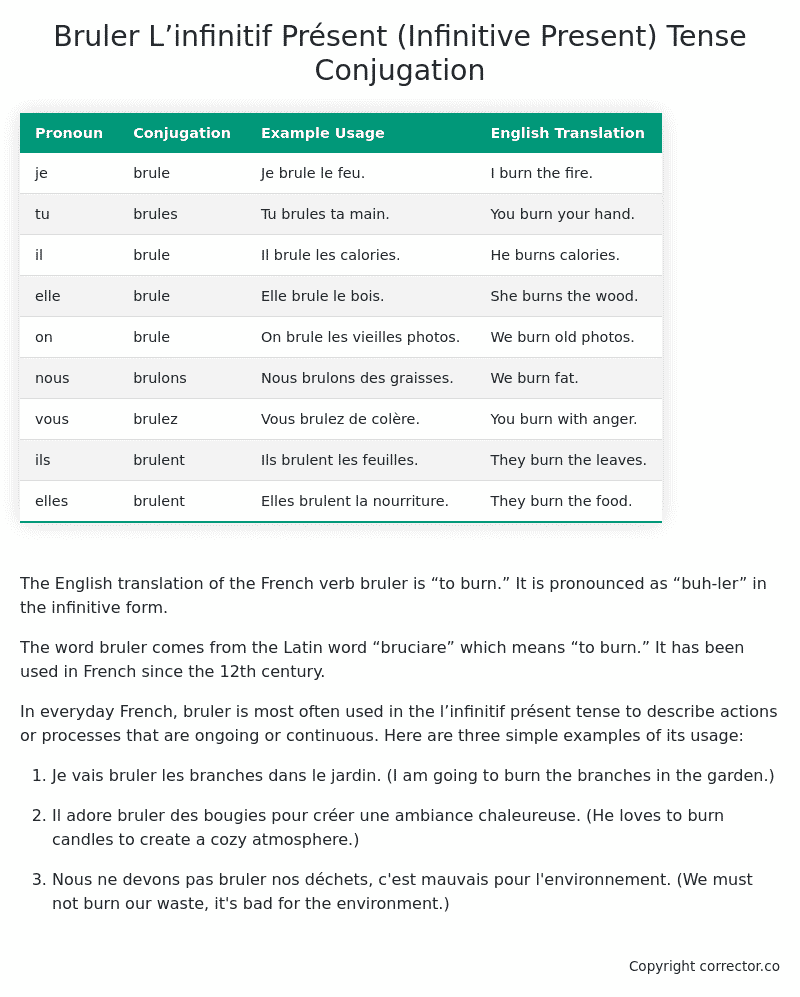
| Pronoun | Conjugation | Example Usage | English Translation |
|---|---|---|---|
| je | brule | Je brule le feu. | I burn the fire. |
| tu | brules | Tu brules ta main. | You burn your hand. |
| il | brule | Il brule les calories. | He burns calories. |
| elle | brule | Elle brule le bois. | She burns the wood. |
| on | brule | On brule les vieilles photos. | We burn old photos. |
| nous | brulons | Nous brulons des graisses. | We burn fat. |
| vous | brulez | Vous brulez de colère. | You burn with anger. |
| ils | brulent | Ils brulent les feuilles. | They burn the leaves. |
| elles | brulent | Elles brulent la nourriture. | They burn the food. |
Other Conjugations for Bruler.
Le Present (Present Tense) Conjugation of the French Verb bruler
Imparfait (Imperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb bruler
Passé Simple (Simple Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb bruler
Passé Composé (Present Perfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb bruler
Futur Simple (Simple Future) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb bruler
Futur Proche (Near Future) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb bruler
Plus-que-parfait (Pluperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb bruler
Passé Antérieur (Past Anterior) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb bruler
Futur Antérieur (Future Anterior) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb bruler
Subjonctif Présent (Subjunctive Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb bruler
Subjonctif Passé (Subjunctive Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb bruler
Subjonctif Imparfait (Subjunctive Imperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb bruler
Subjonctif Plus-que-parfait (Subjunctive Pluperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb bruler
Conditionnel Présent (Conditional Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb bruler
Conditionnel Passé (Conditional Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb bruler
L’impératif Présent (Imperative Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb bruler
L’infinitif Présent (Infinitive Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb bruler (this article)
Struggling with French verbs or the language in general? Why not use our free French Grammar Checker – no registration required!
Get a FREE Download Study Sheet of this Conjugation 🔥
Simply right click the image below, click “save image” and get your free reference for the bruler L’infinitif Présent tense conjugation!
Bruler – About the French L’infinitif Présent (Infinitive Present) Tense
Forming the Infinitive Present
Common Everyday Usage Patterns
As a Verb’s Dictionary Form
After Modal Verbs
As an Imperative
In Infinitive Clauses
Interactions with Other Tenses
Present Tense
Future Tense
Conditional Tense
Passé Composé
Imperfect Tense
Subjunctive and Conditional Moods
Summary
Want More?
I hope you enjoyed this article on the verb bruler. Still in a learning mood? Check out another TOTALLY random French verb conjugation!


