L’infinitif Présent (Infinitive Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb enjamber
Introduction to the verb enjamber
The English translation of the French verb enjamber is “to straddle” or “to step over.” The infinitive form of enjamber is pronounced as “ahn-zham-bay.”
Enjamber comes from the Old French word “enjambe,” which means “to straddle.” It is derived from the Latin root “in” meaning “in” and “gamba” meaning “leg.” In everyday French, enjamber is most often used in the L’infinitif Présent tense to describe physically stepping over something, such as a barrier or obstacle.
Here are three examples of enjamber in L’infinitif Présent tense with their respective English translations:
- Je dois enjamber cette clôture pour entrer dans le jardin. (I have to step over this fence to enter the garden.)
- Elle a enjambé la flaque d’eau pour ne pas se mouiller les pieds. (She straddled the puddle to avoid getting her feet wet.)
- Nous allons devoir enjamber cette rivière pour arriver au village. (We will have to straddle this river to reach the village.)
Table of the L’infinitif Présent (Infinitive Present) Tense Conjugation of enjamber
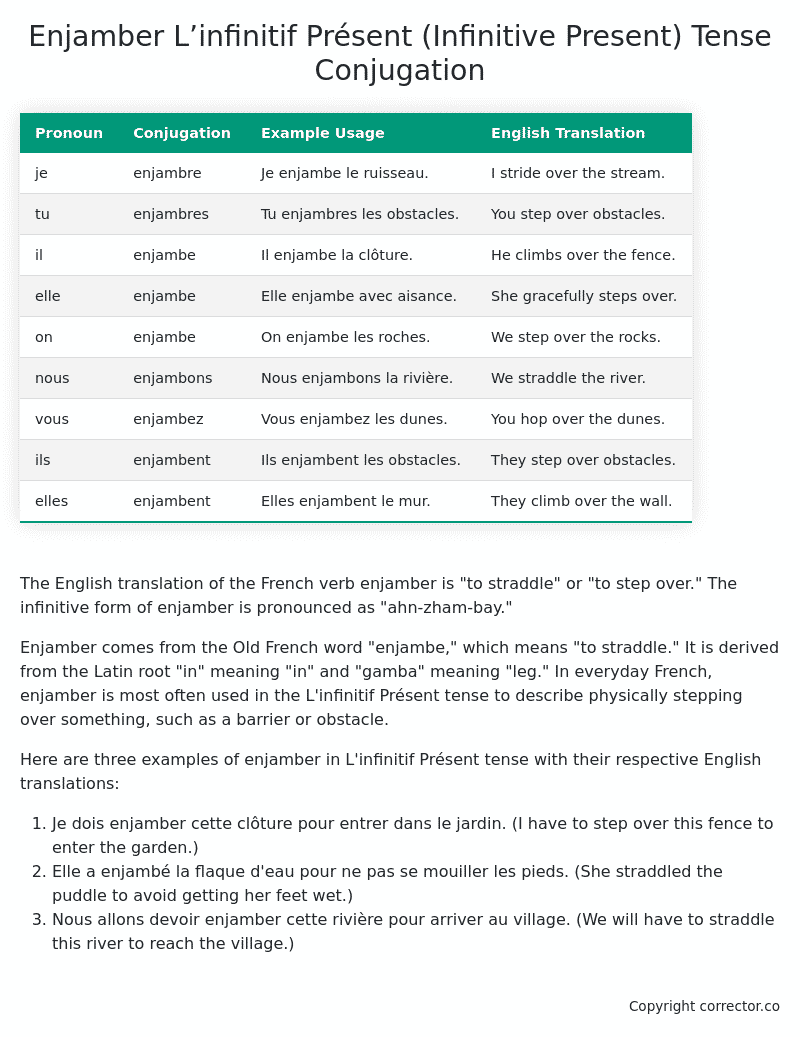
| Pronoun | Conjugation | Example Usage | English Translation |
|---|---|---|---|
| je | enjambre | Je enjambe le ruisseau. | I stride over the stream. |
| tu | enjambres | Tu enjambres les obstacles. | You step over obstacles. |
| il | enjambe | Il enjambe la clôture. | He climbs over the fence. |
| elle | enjambe | Elle enjambe avec aisance. | She gracefully steps over. |
| on | enjambe | On enjambe les roches. | We step over the rocks. |
| nous | enjambons | Nous enjambons la rivière. | We straddle the river. |
| vous | enjambez | Vous enjambez les dunes. | You hop over the dunes. |
| ils | enjambent | Ils enjambent les obstacles. | They step over obstacles. |
| elles | enjambent | Elles enjambent le mur. | They climb over the wall. |
Other Conjugations for Enjamber.
Le Present (Present Tense) Conjugation of the French Verb enjamber
Imparfait (Imperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb enjamber
Passé Simple (Simple Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb enjamber
Passé Composé (Present Perfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb enjamber
Futur Simple (Simple Future) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb enjamber
Futur Proche (Near Future) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb enjamber
Plus-que-parfait (Pluperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb enjamber
Passé Antérieur (Past Anterior) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb enjamber
Futur Antérieur (Future Anterior) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb enjamber
Subjonctif Présent (Subjunctive Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb enjamber
Subjonctif Passé (Subjunctive Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb enjamber
Subjonctif Imparfait (Subjunctive Imperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb enjamber
Subjonctif Plus-que-parfait (Subjunctive Pluperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb enjamber
Conditionnel Présent (Conditional Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb enjamber
Conditionnel Passé (Conditional Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb enjamber
L’impératif Présent (Imperative Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb enjamber
L’infinitif Présent (Infinitive Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb enjamber (this article)
Struggling with French verbs or the language in general? Why not use our free French Grammar Checker – no registration required!
Get a FREE Download Study Sheet of this Conjugation 🔥
Simply right click the image below, click “save image” and get your free reference for the enjamber L’infinitif Présent tense conjugation!
Enjamber – About the French L’infinitif Présent (Infinitive Present) Tense
Forming the Infinitive Present
Common Everyday Usage Patterns
As a Verb’s Dictionary Form
After Modal Verbs
As an Imperative
In Infinitive Clauses
Interactions with Other Tenses
Present Tense
Future Tense
Conditional Tense
Passé Composé
Imperfect Tense
Subjunctive and Conditional Moods
Summary
Want More?
I hope you enjoyed this article on the verb enjamber. Still in a learning mood? Check out another TOTALLY random French verb conjugation!


