Plus-que-parfait (Pluperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb adopter
Introduction to the verb adopter
The English translation of the French verb adopter is “to adopt.” It is pronounced “ah-dop-teh” in its infinitive form.
The verb adopter is derived from the Latin word “adoptare,” meaning “choose” or “take for oneself.” It entered the French language in the 14th century and has been commonly used since then.
In everyday French, adopter is most often used in the Plus-que-parfait tense, which is the past tense used to express an action that occurred before another past action. It is formed using the auxiliary verb “avoir” or “être” in the imperfect tense, followed by the past participle of adopter (adopté).
Here are three examples of adopter being used in the Plus-que-parfait tense in everyday French:
- J’avais adopté un chat avant d’avoir un chien. (I had adopted a cat before getting a dog.)
- Ils étaient déjà adoptés par une famille aimante. (They had already been adopted by a loving family.)
- Elle avait adopté un régime végétarien avant de devenir vegan. (She had adopted a vegetarian diet before becoming vegan.)
In these examples, the verb adopter is used to describe a completed action that happened before another past action. It is often used to talk about decisions or choices that were made in the past. The English translations for these sentences also use the past perfect tense to convey the same meaning.
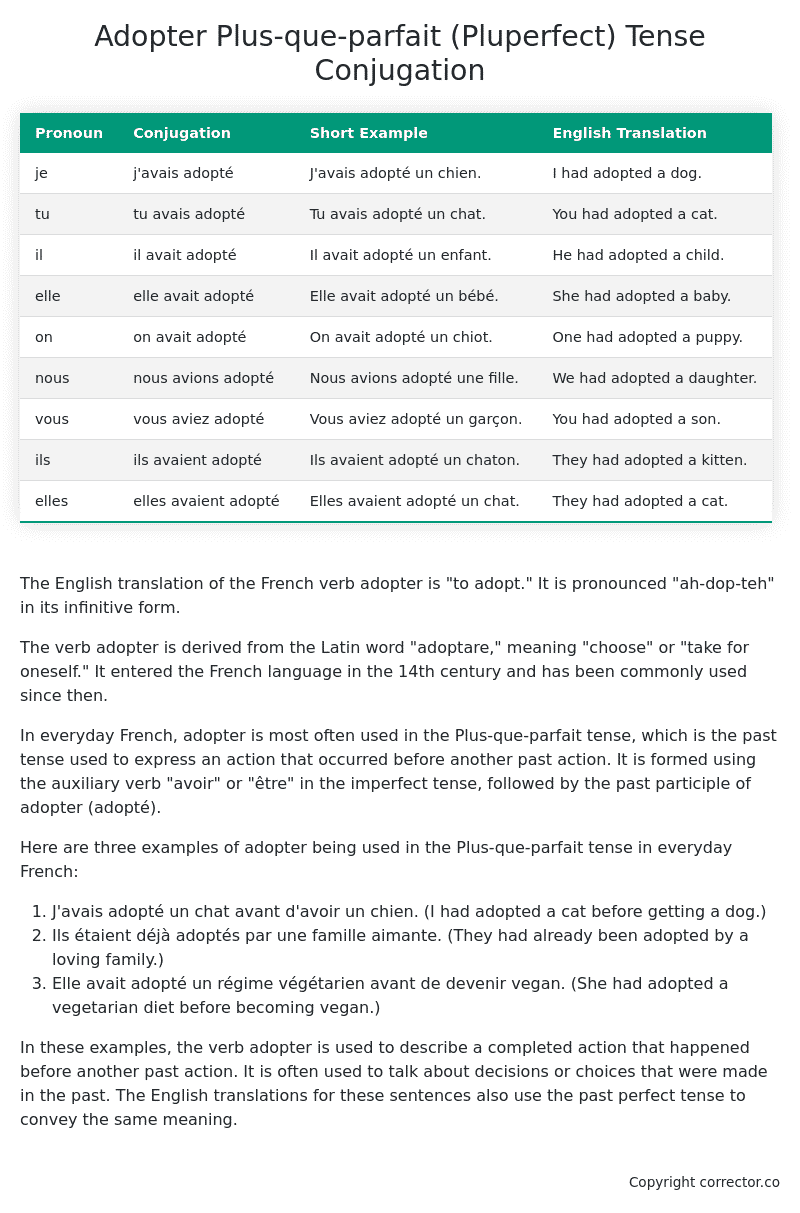
Table of the Plus-que-parfait (Pluperfect) Tense Conjugation of adopter
| Pronoun | Conjugation | Short Example | English Translation |
|---|---|---|---|
| je | j’avais adopté | J’avais adopté un chien. | I had adopted a dog. |
| tu | tu avais adopté | Tu avais adopté un chat. | You had adopted a cat. |
| il | il avait adopté | Il avait adopté un enfant. | He had adopted a child. |
| elle | elle avait adopté | Elle avait adopté un bébé. | She had adopted a baby. |
| on | on avait adopté | On avait adopté un chiot. | One had adopted a puppy. |
| nous | nous avions adopté | Nous avions adopté une fille. | We had adopted a daughter. |
| vous | vous aviez adopté | Vous aviez adopté un garçon. | You had adopted a son. |
| ils | ils avaient adopté | Ils avaient adopté un chaton. | They had adopted a kitten. |
| elles | elles avaient adopté | Elles avaient adopté un chat. | They had adopted a cat. |
Other Conjugations for Adopter.
Le Present (Present Tense) Conjugation of the French Verb adopter
Imparfait (Imperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb adopter
Passé Simple (Simple Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb adopter
Passé Composé (Present Perfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb adopter
Futur Simple (Simple Future) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb adopter
Futur Proche (Near Future) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb adopter
Plus-que-parfait (Pluperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb adopter (this article)
Passé Antérieur (Past Anterior) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb adopter
Futur Antérieur (Future Anterior) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb adopter
Subjonctif Présent (Subjunctive Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb adopter
Subjonctif Passé (Subjunctive Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb adopter
Subjonctif Imparfait (Subjunctive Imperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb adopter
Subjonctif Plus-que-parfait (Subjunctive Pluperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb adopter
Conditionnel Présent (Conditional Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb adopter
Conditionnel Passé (Conditional Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb adopter
L’impératif Présent (Imperative Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb adopter
L’infinitif Présent (Infinitive Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb adopter
Struggling with French verbs or the language in general? Why not use our free French Grammar Checker – no registration required!
Get a FREE Download Study Sheet of this Conjugation 🔥
Simply right click the image below, click “save image” and get your free reference for the adopter Plus-que-parfait tense conjugation!
Adopter – About the French Plus-que-parfait (Pluperfect) Tense
Tense Formation
Common everyday usage patterns
Sequencing of past events
Background information
Hypothetical or reported speech
Interactions with other tenses
Summary
I hope you enjoyed this article on the verb adopter. Still in a learning mood? Check out another TOTALLY random French verb conjugation!


