Plus-que-parfait (Pluperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb badiner
Introduction to the verb badiner
The English translation of the French verb badiner is “to joke” or “to jest.” It is pronounced “ba-dee-neh.”
The language origin of badiner comes from the Old French word “badin,” which means “merry” or “playful.” It is most often used in everyday French in the plus-que-parfait tense, which expresses an action that was completed in the past before another past action.
Examples:
-
Hier, je badinais avec mes amis avant de partir en vacances. (Yesterday, I was joking with my friends before leaving for vacation.)
-
Elle avait badiné avec lui pendant des mois avant de se rendre compte qu’il était sérieux. (She had been joking with him for months before realizing he was serious.)
-
Le professeur avait réprimandé les élèves qui avaient badiné pendant le cours. (The teacher had scolded the students who had been joking during class.)
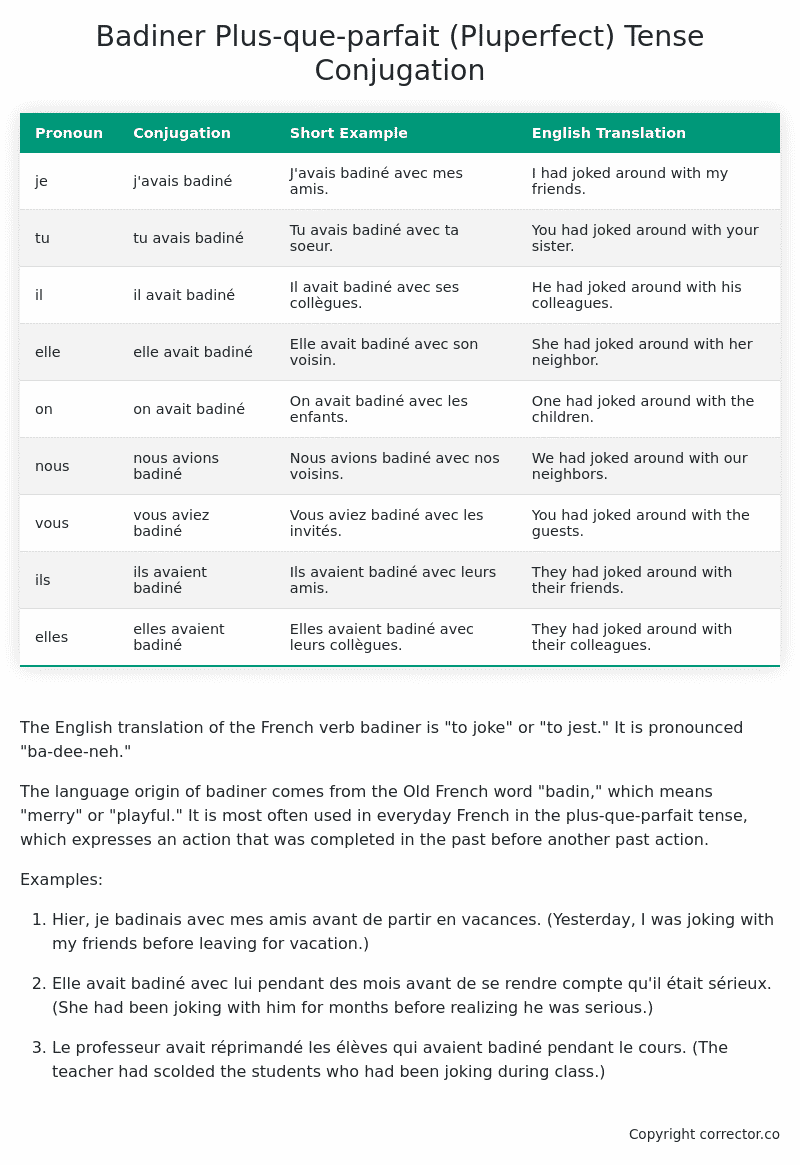
Table of the Plus-que-parfait (Pluperfect) Tense Conjugation of badiner
| Pronoun | Conjugation | Short Example | English Translation |
|---|---|---|---|
| je | j’avais badiné | J’avais badiné avec mes amis. | I had joked around with my friends. |
| tu | tu avais badiné | Tu avais badiné avec ta soeur. | You had joked around with your sister. |
| il | il avait badiné | Il avait badiné avec ses collègues. | He had joked around with his colleagues. |
| elle | elle avait badiné | Elle avait badiné avec son voisin. | She had joked around with her neighbor. |
| on | on avait badiné | On avait badiné avec les enfants. | One had joked around with the children. |
| nous | nous avions badiné | Nous avions badiné avec nos voisins. | We had joked around with our neighbors. |
| vous | vous aviez badiné | Vous aviez badiné avec les invités. | You had joked around with the guests. |
| ils | ils avaient badiné | Ils avaient badiné avec leurs amis. | They had joked around with their friends. |
| elles | elles avaient badiné | Elles avaient badiné avec leurs collègues. | They had joked around with their colleagues. |
Other Conjugations for Badiner.
Le Present (Present Tense) Conjugation of the French Verb badiner
Imparfait (Imperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb badiner
Passé Simple (Simple Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb badiner
Passé Composé (Present Perfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb badiner
Futur Simple (Simple Future) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb badiner
Futur Proche (Near Future) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb badiner
Plus-que-parfait (Pluperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb badiner (this article)
Passé Antérieur (Past Anterior) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb badiner
Futur Antérieur (Future Anterior) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb badiner
Subjonctif Présent (Subjunctive Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb badiner
Subjonctif Passé (Subjunctive Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb badiner
Subjonctif Imparfait (Subjunctive Imperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb badiner
Subjonctif Plus-que-parfait (Subjunctive Pluperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb badiner
Conditionnel Présent (Conditional Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb badiner
Conditionnel Passé (Conditional Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb badiner
L’impératif Présent (Imperative Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb badiner
L’infinitif Présent (Infinitive Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb badiner
Struggling with French verbs or the language in general? Why not use our free French Grammar Checker – no registration required!
Get a FREE Download Study Sheet of this Conjugation 🔥
Simply right click the image below, click “save image” and get your free reference for the badiner Plus-que-parfait tense conjugation!
Badiner – About the French Plus-que-parfait (Pluperfect) Tense
Tense Formation
Common everyday usage patterns
Sequencing of past events
Background information
Hypothetical or reported speech
Interactions with other tenses
Summary
I hope you enjoyed this article on the verb badiner. Still in a learning mood? Check out another TOTALLY random French verb conjugation!


