Plus-que-parfait (Pluperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb contre-plaquer
Introduction to the verb contre-plaquer
The English translation of the French verb contre-plaquer is “to counter-check” or “to oppose”. It is pronounced “kawn-truh-plah-kay”.
The verb contre-plaquer is derived from the French words “contre” meaning “against” and “plaquer” meaning “to check”. It is most often used in everyday French in the Plus-que-parfait tense, which is the past perfect tense. This tense is used to describe an action that was completed before another past action.
Examples of contre-plaquer in the Plus-que-parfait tense:
- J’avais contre-plaqué ses idées avant qu’il ne prenne une décision. (I had opposed his ideas before he made a decision.)
- Ils avaient contre-plaqué les arguments de l’autre équipe avant le début du match. (They had countered the arguments of the other team before the start of the game.)
- Tu avais contre-plaqué mes plans pour la soirée en proposant une autre activité. (You had thwarted my plans for the evening by suggesting another activity.)
Table of the Plus-que-parfait (Pluperfect) Tense Conjugation of contre-plaquer
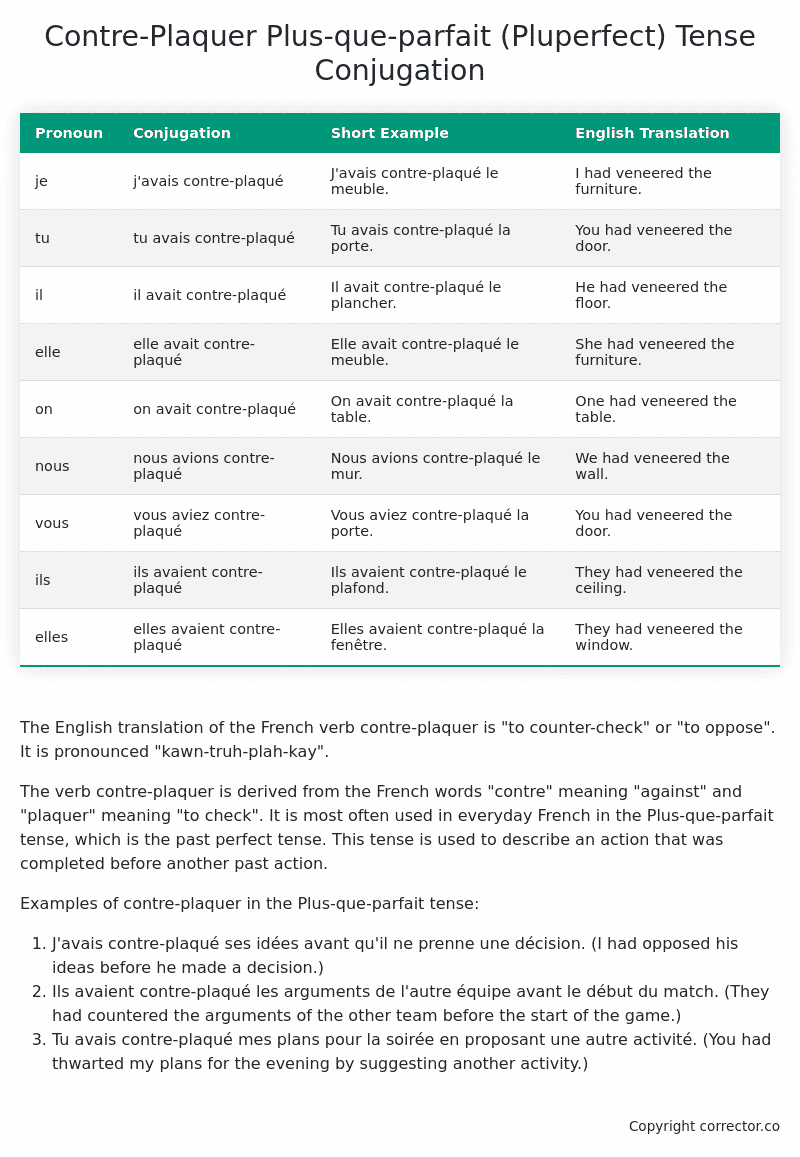
| Pronoun | Conjugation | Short Example | English Translation |
|---|---|---|---|
| je | j’avais contre-plaqué | J’avais contre-plaqué le meuble. | I had veneered the furniture. |
| tu | tu avais contre-plaqué | Tu avais contre-plaqué la porte. | You had veneered the door. |
| il | il avait contre-plaqué | Il avait contre-plaqué le plancher. | He had veneered the floor. |
| elle | elle avait contre-plaqué | Elle avait contre-plaqué le meuble. | She had veneered the furniture. |
| on | on avait contre-plaqué | On avait contre-plaqué la table. | One had veneered the table. |
| nous | nous avions contre-plaqué | Nous avions contre-plaqué le mur. | We had veneered the wall. |
| vous | vous aviez contre-plaqué | Vous aviez contre-plaqué la porte. | You had veneered the door. |
| ils | ils avaient contre-plaqué | Ils avaient contre-plaqué le plafond. | They had veneered the ceiling. |
| elles | elles avaient contre-plaqué | Elles avaient contre-plaqué la fenêtre. | They had veneered the window. |
Other Conjugations for Contre-Plaquer.
Le Present (Present Tense) Conjugation of the French Verb contre-plaquer
Imparfait (Imperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb contre-plaquer
Passé Simple (Simple Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb contre-plaquer
Passé Composé (Present Perfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb contre-plaquer
Futur Simple (Simple Future) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb contre-plaquer
Futur Proche (Near Future) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb contre-plaquer
Plus-que-parfait (Pluperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb contre-plaquer (this article)
Passé Antérieur (Past Anterior) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb contre-plaquer
Futur Antérieur (Future Anterior) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb contre-plaquer
Subjonctif Présent (Subjunctive Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb contre-plaquer
Subjonctif Passé (Subjunctive Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb contre-plaquer
Subjonctif Imparfait (Subjunctive Imperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb contre-plaquer
Conditionnel Présent (Conditional Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb contre-plaquer
Conditionnel Passé (Conditional Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb contre-plaquer
L’impératif Présent (Imperative Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb contre-plaquer
L’infinitif Présent (Infinitive Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb contre-plaquer
Struggling with French verbs or the language in general? Why not use our free French Grammar Checker – no registration required!
Get a FREE Download Study Sheet of this Conjugation 🔥
Simply right click the image below, click “save image” and get your free reference for the contre-plaquer Plus-que-parfait tense conjugation!
Contre-Plaquer – About the French Plus-que-parfait (Pluperfect) Tense
Tense Formation
Common everyday usage patterns
Sequencing of past events
Background information
Hypothetical or reported speech
Interactions with other tenses
Summary
I hope you enjoyed this article on the verb contre-plaquer. Still in a learning mood? Check out another TOTALLY random French verb conjugation!


