Subjonctif Passé (Subjunctive Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb barguigner
Introduction to the verb barguigner
The English translation of the French verb barguigner is “to haggle” or “to bargain.” It is pronounced as “bar-gee-nye.”
The word barguigner comes from the Old French word “aberjugner” which means “to dispute” or “to argue.” The verb is primarily used in spoken French and is most commonly used in the Subjonctif Passé tense, which is used to express a past hypothetical action or situation.
Examples of its usage in the Subjonctif Passé tense are:
-
Je doute qu’il ait barguigné le prix de la voiture. (I doubt he haggled the price of the car.)
-
Il est possible que nous ayons barguigné avec le vendeur pour obtenir une réduction. (It is possible that we haggled with the seller to get a discount.)
-
J’aurais aimé que tu aies barguigné un peu plus pour avoir une meilleure offre. (I wish you had haggled a bit more to get a better deal.)
In these examples, the Subjonctif Passé tense is used to express an uncertain or hypothetical action in the past. The verb barguigner is often used in this tense to describe the act of negotiating or bargaining, especially in commercial transactions.
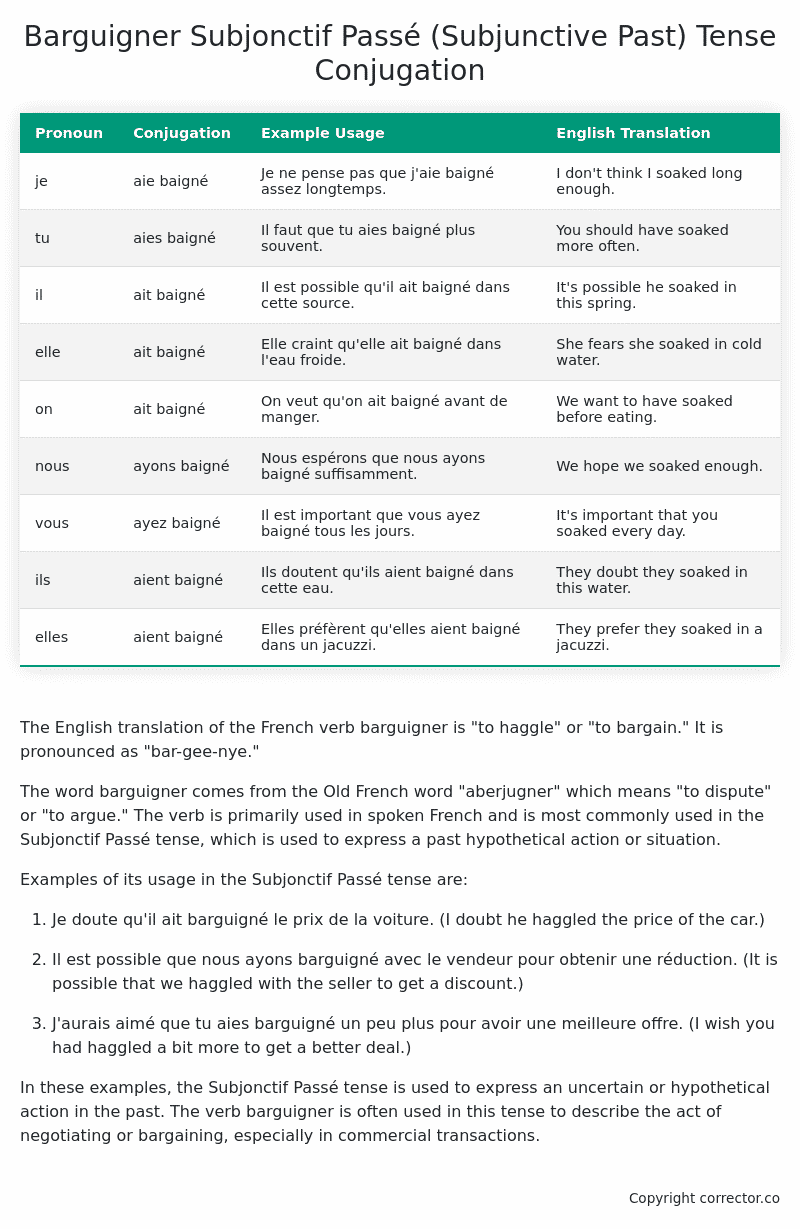
Table of the Subjonctif Passé (Subjunctive Past) Tense Conjugation of barguigner
| Pronoun | Conjugation | Example Usage | English Translation |
|---|---|---|---|
| je | aie baigné | Je ne pense pas que j’aie baigné assez longtemps. | I don’t think I soaked long enough. |
| tu | aies baigné | Il faut que tu aies baigné plus souvent. | You should have soaked more often. |
| il | ait baigné | Il est possible qu’il ait baigné dans cette source. | It’s possible he soaked in this spring. |
| elle | ait baigné | Elle craint qu’elle ait baigné dans l’eau froide. | She fears she soaked in cold water. |
| on | ait baigné | On veut qu’on ait baigné avant de manger. | We want to have soaked before eating. |
| nous | ayons baigné | Nous espérons que nous ayons baigné suffisamment. | We hope we soaked enough. |
| vous | ayez baigné | Il est important que vous ayez baigné tous les jours. | It’s important that you soaked every day. |
| ils | aient baigné | Ils doutent qu’ils aient baigné dans cette eau. | They doubt they soaked in this water. |
| elles | aient baigné | Elles préfèrent qu’elles aient baigné dans un jacuzzi. | They prefer they soaked in a jacuzzi. |
Other Conjugations for Barguigner.
Le Present (Present Tense) Conjugation of the French Verb barguigner
Imparfait (Imperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb barguigner
Passé Simple (Simple Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb barguigner
Passé Composé (Present Perfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb barguigner
Futur Simple (Simple Future) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb barguigner
Futur Proche (Near Future) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb barguigner
Plus-que-parfait (Pluperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb barguigner
Passé Antérieur (Past Anterior) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb barguigner
Futur Antérieur (Future Anterior) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb barguigner
Subjonctif Présent (Subjunctive Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb barguigner
Subjonctif Passé (Subjunctive Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb barguigner (this article)
Subjonctif Imparfait (Subjunctive Imperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb barguigner
Subjonctif Plus-que-parfait (Subjunctive Pluperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb barguigner
Conditionnel Présent (Conditional Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb barguigner
Conditionnel Passé (Conditional Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb barguigner
L’impératif Présent (Imperative Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb barguigner
L’infinitif Présent (Infinitive Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb barguigner
Struggling with French verbs or the language in general? Why not use our free French Grammar Checker – no registration required!
Get a FREE Download Study Sheet of this Conjugation 🔥
Simply right click the image below, click “save image” and get your free reference for the barguigner Subjonctif Passé tense conjugation!
Barguigner – About the French Subjonctif Passé (Subjunctive Past) Tense
Formation of the Subjonctif Passé
Everyday Usage Patterns
Interactions with Other Tenses
Present tense
Future tense
Conditional
Summary
I hope you enjoyed this article on the verb barguigner. Still in a learning mood? Check out another TOTALLY random French verb conjugation!


