Subjonctif Passé (Subjunctive Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb capeyer
Introduction to the verb capeyer
The English translation of the French verb capeyer is “to deceive” or “to cheat.” It is pronounced like “kah-peh-yay.”
The language origin of capeyer can be traced back to the Latin word “caper” which means “goat.” Over the years, it evolved to mean “to deceive or trick someone like a goat does with its horns.” In everyday French, capeyer is used in the Subjonctif Passé tense to express a past action that is uncertain or hypothetical.
Here are three simple examples of capeyer in the Subjonctif Passé tense with their respective English translations:
- J’espère qu’il n’a pas encore capeyé ses parents. (I hope he hasn’t deceived his parents yet.)
- Il aurait mieux fait de ne pas me capeyer. (He should not have deceived me.)
- Nous craignons qu’il ait capeyé le juge pour échapper à la justice. (We fear he may have deceived the judge to escape justice.)
Table of the Subjonctif Passé (Subjunctive Past) Tense Conjugation of capeyer
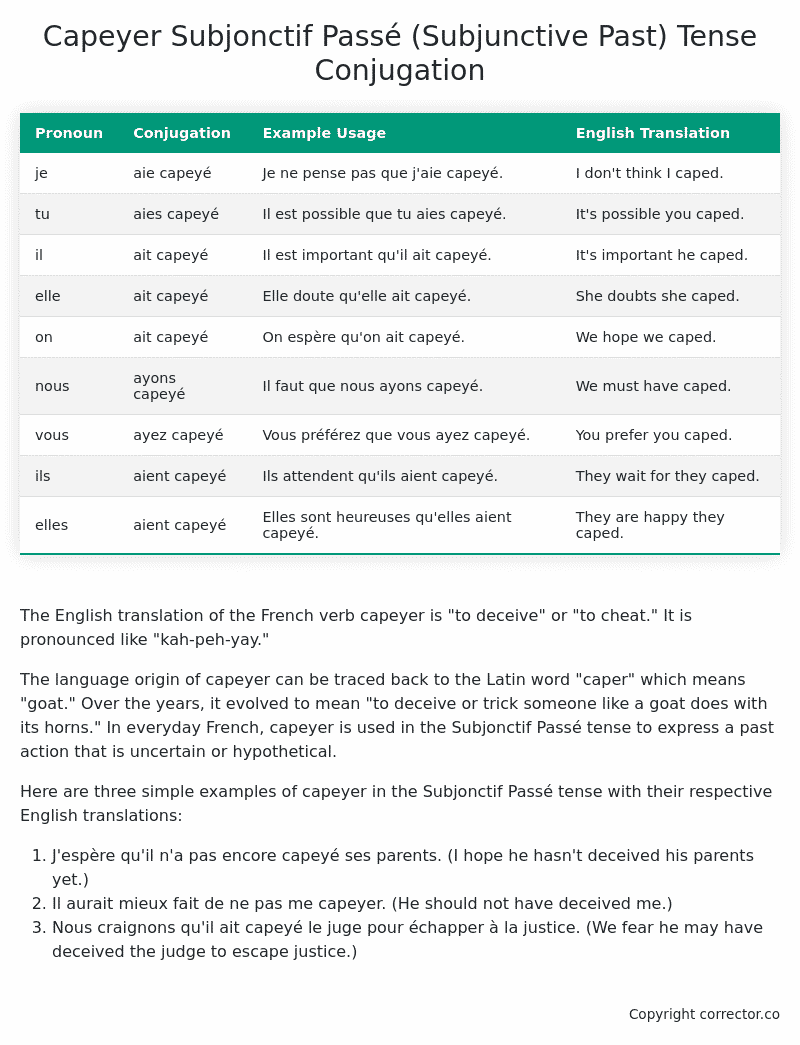
| Pronoun | Conjugation | Example Usage | English Translation |
|---|---|---|---|
| je | aie capeyé | Je ne pense pas que j’aie capeyé. | I don’t think I caped. |
| tu | aies capeyé | Il est possible que tu aies capeyé. | It’s possible you caped. |
| il | ait capeyé | Il est important qu’il ait capeyé. | It’s important he caped. |
| elle | ait capeyé | Elle doute qu’elle ait capeyé. | She doubts she caped. |
| on | ait capeyé | On espère qu’on ait capeyé. | We hope we caped. |
| nous | ayons capeyé | Il faut que nous ayons capeyé. | We must have caped. |
| vous | ayez capeyé | Vous préférez que vous ayez capeyé. | You prefer you caped. |
| ils | aient capeyé | Ils attendent qu’ils aient capeyé. | They wait for they caped. |
| elles | aient capeyé | Elles sont heureuses qu’elles aient capeyé. | They are happy they caped. |
Other Conjugations for Capeyer.
Le Present (Present Tense) Conjugation of the French Verb capeyer
Imparfait (Imperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb capeyer
Passé Simple (Simple Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb capeyer
Passé Composé (Present Perfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb capeyer
Futur Simple (Simple Future) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb capeyer
Futur Proche (Near Future) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb capeyer
Plus-que-parfait (Pluperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb capeyer
Passé Antérieur (Past Anterior) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb capeyer
Futur Antérieur (Future Anterior) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb capeyer
Subjonctif Présent (Subjunctive Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb capeyer
Subjonctif Passé (Subjunctive Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb capeyer (this article)
Subjonctif Imparfait (Subjunctive Imperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb capeyer
Subjonctif Plus-que-parfait (Subjunctive Pluperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb capeyer
Conditionnel Présent (Conditional Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb capeyer
Conditionnel Passé (Conditional Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb capeyer
L’impératif Présent (Imperative Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb capeyer
L’infinitif Présent (Infinitive Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb capeyer
Struggling with French verbs or the language in general? Why not use our free French Grammar Checker – no registration required!
Get a FREE Download Study Sheet of this Conjugation 🔥
Simply right click the image below, click “save image” and get your free reference for the capeyer Subjonctif Passé tense conjugation!
Capeyer – About the French Subjonctif Passé (Subjunctive Past) Tense
Formation of the Subjonctif Passé
Everyday Usage Patterns
Interactions with Other Tenses
Present tense
Future tense
Conditional
Summary
I hope you enjoyed this article on the verb capeyer. Still in a learning mood? Check out another TOTALLY random French verb conjugation!


