Futur Antérieur (Future Anterior) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb exiler
Introduction to the verb exiler
The English translation of the French verb exiler is “to exile.” It is pronounced as “ehk-see-leh” in its infinitive form.
The word exiler comes from the Latin word “exilium,” meaning “banishment” or “exile.” It entered the French language in the 13th century. In everyday French, it is most often used to describe the act of forcing someone to leave their home country or to live in a foreign land as a form of punishment or as a result of political or social issues.
In the Futur Antérieur tense, exiler is used to describe an action that will have been completed in the future. Here are three simple examples of its usage in this tense:
- Je l’aurai exilé avant son prochain anniversaire. (I will have exiled him before his next birthday.)
- Le gouvernement aura exilé tous les opposants politiques d’ici la fin de l’année. (The government will have exiled all political opponents by the end of the year.)
- Les colons auront exilé les autochtones vers des terres plus arides. (The settlers will have exiled the indigenous people to more arid lands.)
Note: In these examples, the auxiliary verb “avoir” is used before the past participle “exilé” to form the Futur Antérieur tense.
In all of these examples, the English translation remains the same: “to have exiled.” This tense is often used to talk about events or actions that will happen in the future and will be completed before another specific event or time in the future.
Table of the Futur Antérieur (Future Anterior) Tense Conjugation of exiler
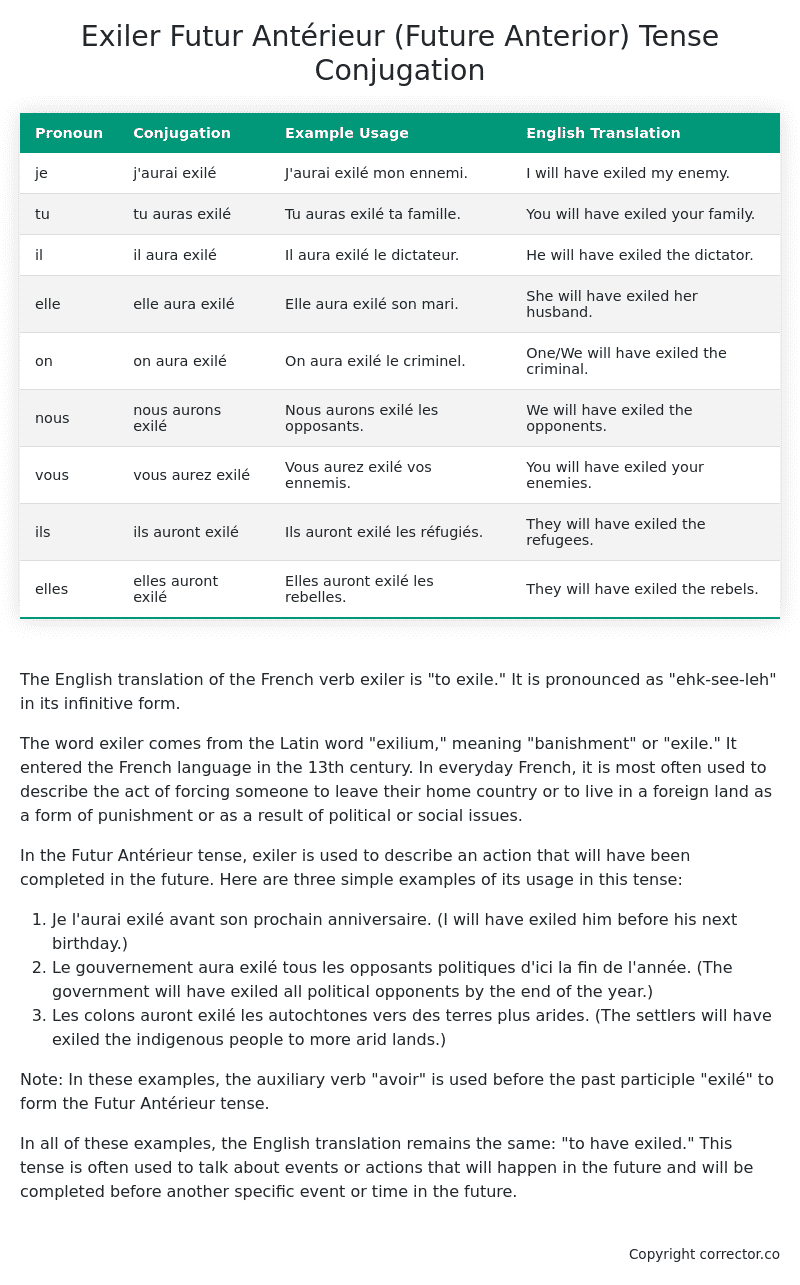
| Pronoun | Conjugation | Example Usage | English Translation |
|---|---|---|---|
| je | j’aurai exilé | J’aurai exilé mon ennemi. | I will have exiled my enemy. |
| tu | tu auras exilé | Tu auras exilé ta famille. | You will have exiled your family. |
| il | il aura exilé | Il aura exilé le dictateur. | He will have exiled the dictator. |
| elle | elle aura exilé | Elle aura exilé son mari. | She will have exiled her husband. |
| on | on aura exilé | On aura exilé le criminel. | One/We will have exiled the criminal. |
| nous | nous aurons exilé | Nous aurons exilé les opposants. | We will have exiled the opponents. |
| vous | vous aurez exilé | Vous aurez exilé vos ennemis. | You will have exiled your enemies. |
| ils | ils auront exilé | Ils auront exilé les réfugiés. | They will have exiled the refugees. |
| elles | elles auront exilé | Elles auront exilé les rebelles. | They will have exiled the rebels. |
Other Conjugations for Exiler.
Le Present (Present Tense) Conjugation of the French Verb exiler
Imparfait (Imperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb exiler
Passé Simple (Simple Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb exiler
Passé Composé (Present Perfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb exiler
Futur Simple (Simple Future) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb exiler
Futur Proche (Near Future) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb exiler
Plus-que-parfait (Pluperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb exiler
Passé Antérieur (Past Anterior) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb exiler
Futur Antérieur (Future Anterior) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb exiler (this article)
Subjonctif Présent (Subjunctive Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb exiler
Subjonctif Passé (Subjunctive Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb exiler
Subjonctif Imparfait (Subjunctive Imperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb exiler
Subjonctif Plus-que-parfait (Subjunctive Pluperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb exiler
Conditionnel Présent (Conditional Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb exiler
Conditionnel Passé (Conditional Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb exiler
L’impératif Présent (Imperative Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb exiler
L’infinitif Présent (Infinitive Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb exiler
Struggling with French verbs or the language in general? Why not use our free French Grammar Checker – no registration required!
Get a FREE Download Study Sheet of this Conjugation 🔥
Simply right click the image below, click “save image” and get your free reference for the exiler Futur Antérieur tense conjugation!
Exiler – About the French Futur Antérieur (Future Anterior) Tense
Construction
Common Everyday Usage Patterns
Interactions with Other Tenses
For example
Summary
I hope you enjoyed this article on the verb exiler. Still in a learning mood? Check out another TOTALLY random French verb conjugation!


