Futur Antérieur (Future Anterior) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb gargouiller
Introduction to the verb gargouiller
The English translation of the French verb gargouiller is “to gurgle.” The infinitive form of gargouiller is pronounced “gar-goo-yay.”
The word gargouiller comes from the Old French word “gargouille,” which referred to the sound that water makes when it runs through pipes or channels. It is most often used in everyday French to describe the sound of a liquid flowing or bubbling, or the sound of one’s stomach growling.
In the Futur Antérieur tense, gargouiller is used to describe an action that will have already happened in the future. It is formed by using the future tense of the auxiliary verb “avoir” (aurai, auras, aura, aurons, aurez, auront) + the past participle of gargouiller, which is “gargouillé.”
Three simple examples of gargouiller in the Futur Antérieur tense are:
- Je vais avoir gargouillé après avoir mangé cette soupe épicée. (I will have gurgled after eating this spicy soup.)
- Tu auras gargouillé pendant le long trajet en voiture. (You will have gurgled during the long car ride.)
- Ils auront gargouillé toute la nuit à cause de leur repas trop copieux. (They will have gurgled all night because of their heavy meal.)
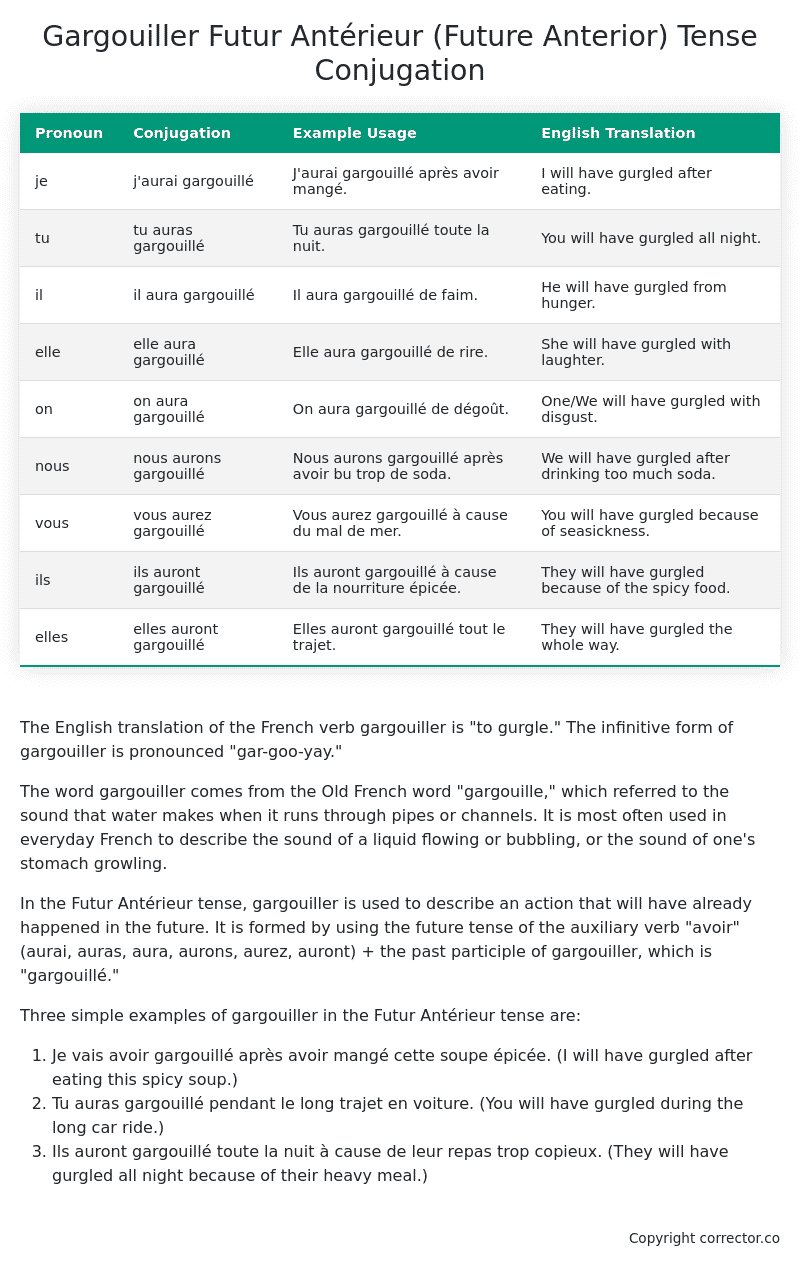
Table of the Futur Antérieur (Future Anterior) Tense Conjugation of gargouiller
| Pronoun | Conjugation | Example Usage | English Translation |
|---|---|---|---|
| je | j’aurai gargouillé | J’aurai gargouillé après avoir mangé. | I will have gurgled after eating. |
| tu | tu auras gargouillé | Tu auras gargouillé toute la nuit. | You will have gurgled all night. |
| il | il aura gargouillé | Il aura gargouillé de faim. | He will have gurgled from hunger. |
| elle | elle aura gargouillé | Elle aura gargouillé de rire. | She will have gurgled with laughter. |
| on | on aura gargouillé | On aura gargouillé de dégoût. | One/We will have gurgled with disgust. |
| nous | nous aurons gargouillé | Nous aurons gargouillé après avoir bu trop de soda. | We will have gurgled after drinking too much soda. |
| vous | vous aurez gargouillé | Vous aurez gargouillé à cause du mal de mer. | You will have gurgled because of seasickness. |
| ils | ils auront gargouillé | Ils auront gargouillé à cause de la nourriture épicée. | They will have gurgled because of the spicy food. |
| elles | elles auront gargouillé | Elles auront gargouillé tout le trajet. | They will have gurgled the whole way. |
Other Conjugations for Gargouiller.
Le Present (Present Tense) Conjugation of the French Verb gargouiller
Imparfait (Imperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb gargouiller
Passé Simple (Simple Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb gargouiller
Passé Composé (Present Perfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb gargouiller
Futur Simple (Simple Future) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb gargouiller
Futur Proche (Near Future) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb gargouiller
Plus-que-parfait (Pluperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb gargouiller
Passé Antérieur (Past Anterior) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb gargouiller
Futur Antérieur (Future Anterior) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb gargouiller (this article)
Subjonctif Présent (Subjunctive Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb gargouiller
Subjonctif Passé (Subjunctive Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb gargouiller
Subjonctif Imparfait (Subjunctive Imperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb gargouiller
Conditionnel Présent (Conditional Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb gargouiller
Conditionnel Passé (Conditional Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb gargouiller
L’impératif Présent (Imperative Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb gargouiller
L’infinitif Présent (Infinitive Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb gargouiller
Struggling with French verbs or the language in general? Why not use our free French Grammar Checker – no registration required!
Get a FREE Download Study Sheet of this Conjugation 🔥
Simply right click the image below, click “save image” and get your free reference for the gargouiller Futur Antérieur tense conjugation!
Gargouiller – About the French Futur Antérieur (Future Anterior) Tense
Construction
Common Everyday Usage Patterns
Interactions with Other Tenses
For example
Summary
I hope you enjoyed this article on the verb gargouiller. Still in a learning mood? Check out another TOTALLY random French verb conjugation!


