L’impératif Présent (Imperative Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb bosser
Introduction to the verb bosser
The English translation of the French verb bosser is “to work.” It is pronounced as “boh-seh” in its infinitive form.
The word bosser comes from the regional French word “bos” which means “to work hard.” It was first recorded in the French language in the 19th century and was initially used in an informal or slang context. However, over time, it has become a commonly used verb in everyday French, particularly in spoken language.
In the L’impératif Présent tense, bosser is used to give commands or orders. It is often used in a casual or informal way, similar to the English verb “to hustle.” Here are three examples of its usage in this tense:
- Bosse plus vite ! (Work faster!)
- Ne bosse pas trop tard ce soir. (Don’t work too late tonight.)
- Bosse dur et tu réussiras. (Work hard and you will succeed.)
Table of the L’impératif Présent (Imperative Present) Tense Conjugation of bosser
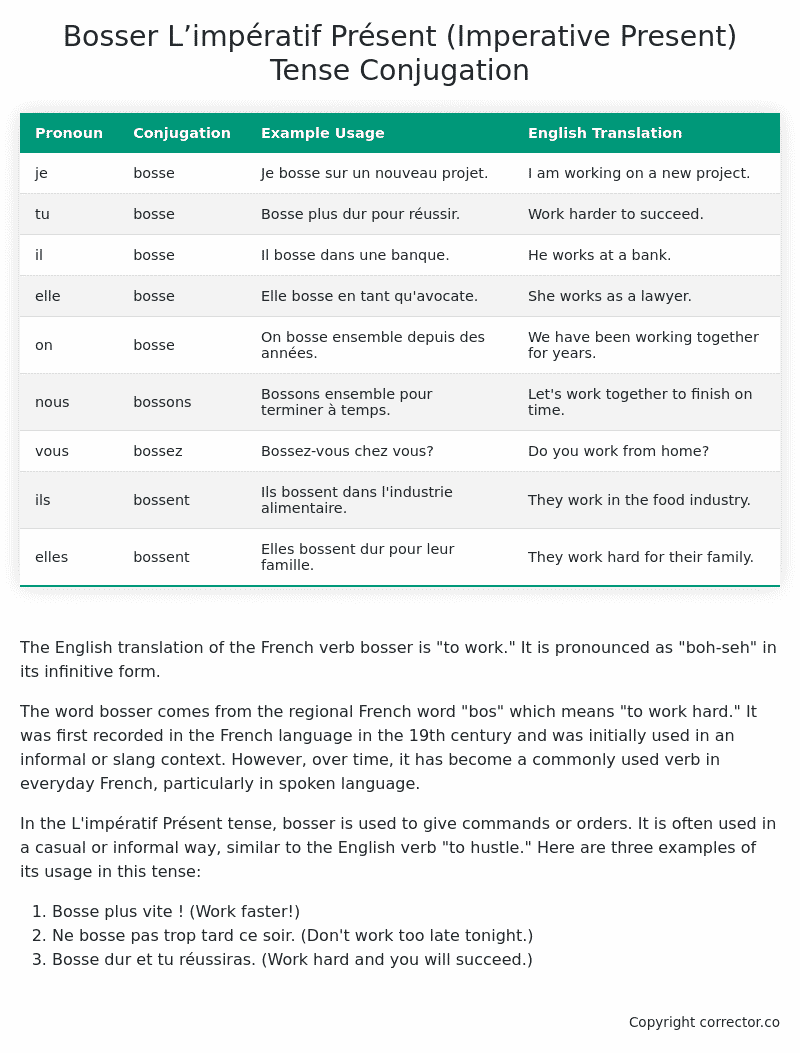
| Pronoun | Conjugation | Example Usage | English Translation |
|---|---|---|---|
| je | bosse | Je bosse sur un nouveau projet. | I am working on a new project. |
| tu | bosse | Bosse plus dur pour réussir. | Work harder to succeed. |
| il | bosse | Il bosse dans une banque. | He works at a bank. |
| elle | bosse | Elle bosse en tant qu’avocate. | She works as a lawyer. |
| on | bosse | On bosse ensemble depuis des années. | We have been working together for years. |
| nous | bossons | Bossons ensemble pour terminer à temps. | Let’s work together to finish on time. |
| vous | bossez | Bossez-vous chez vous? | Do you work from home? |
| ils | bossent | Ils bossent dans l’industrie alimentaire. | They work in the food industry. |
| elles | bossent | Elles bossent dur pour leur famille. | They work hard for their family. |
Other Conjugations for Bosser.
Le Present (Present Tense) Conjugation of the French Verb bosser
Imparfait (Imperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb bosser
Passé Simple (Simple Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb bosser
Passé Composé (Present Perfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb bosser
Futur Simple (Simple Future) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb bosser
Futur Proche (Near Future) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb bosser
Plus-que-parfait (Pluperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb bosser
Passé Antérieur (Past Anterior) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb bosser
Futur Antérieur (Future Anterior) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb bosser
Subjonctif Présent (Subjunctive Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb bosser
Subjonctif Passé (Subjunctive Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb bosser
Subjonctif Imparfait (Subjunctive Imperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb bosser
Subjonctif Plus-que-parfait (Subjunctive Pluperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb bosser
Conditionnel Présent (Conditional Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb bosser
Conditionnel Passé (Conditional Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb bosser
L’impératif Présent (Imperative Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb bosser (this article)
L’infinitif Présent (Infinitive Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb bosser
Struggling with French verbs or the language in general? Why not use our free French Grammar Checker – no registration required!
Get a FREE Download Study Sheet of this Conjugation 🔥
Simply right click the image below, click “save image” and get your free reference for the bosser L’impératif Présent tense conjugation!
Bosser – About the French L’impératif Présent (Imperative Present) Tense
Usage
Giving commands
Making requests
Offering advice
Expressing desires
Conjugation Formation
Interactions with other tenses
Want More?
I hope you enjoyed this article on the verb bosser. Still in a learning mood? Check out another TOTALLY random French verb conjugation!


