Passé Composé (Present Perfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb barricader
Introduction to the verb barricader
The English translation of the French verb barricader is “to barricade.” It is pronounced as bah-ree-kah-deh in the infinitive form.
The word barricader is derived from the Old French word “barricade,” which comes from the Spanish word “barricada,” meaning “barricade” or “obstacle.” It originated from the Latin word “barrica,” meaning “barrel,” as barrels were often used to create barricades in medieval times.
In everyday French, barricader is most often used in the Passé Composé tense, which is the equivalent of the Present Perfect tense in English. This tense is formed by using the auxiliary verb “avoir” (to have) or “être” (to be) and the past participle of the verb, which in this case is “barricadé” for both auxiliary verbs.
Examples of barricader in the Passé Composé tense:
- Nous avons barricadé la porte pour empêcher les voleurs d’entrer. (We barricaded the door to prevent thieves from entering.)
- Les manifestants se sont barricadés dans l’hôtel pour protester contre le gouvernement. (The protesters barricaded themselves in the hotel to protest against the government.)
- J’ai vu que tu as barricadé toutes les fenêtres de ta maison avant la tempête. (I saw that you barricaded all the windows of your house before the storm.)
Overall, barricader is used in the Passé Composé tense to describe a past action of creating a barricade or obstacle for protection or defense.
Table of the Passé Composé (Present Perfect) Tense Conjugation of barricader
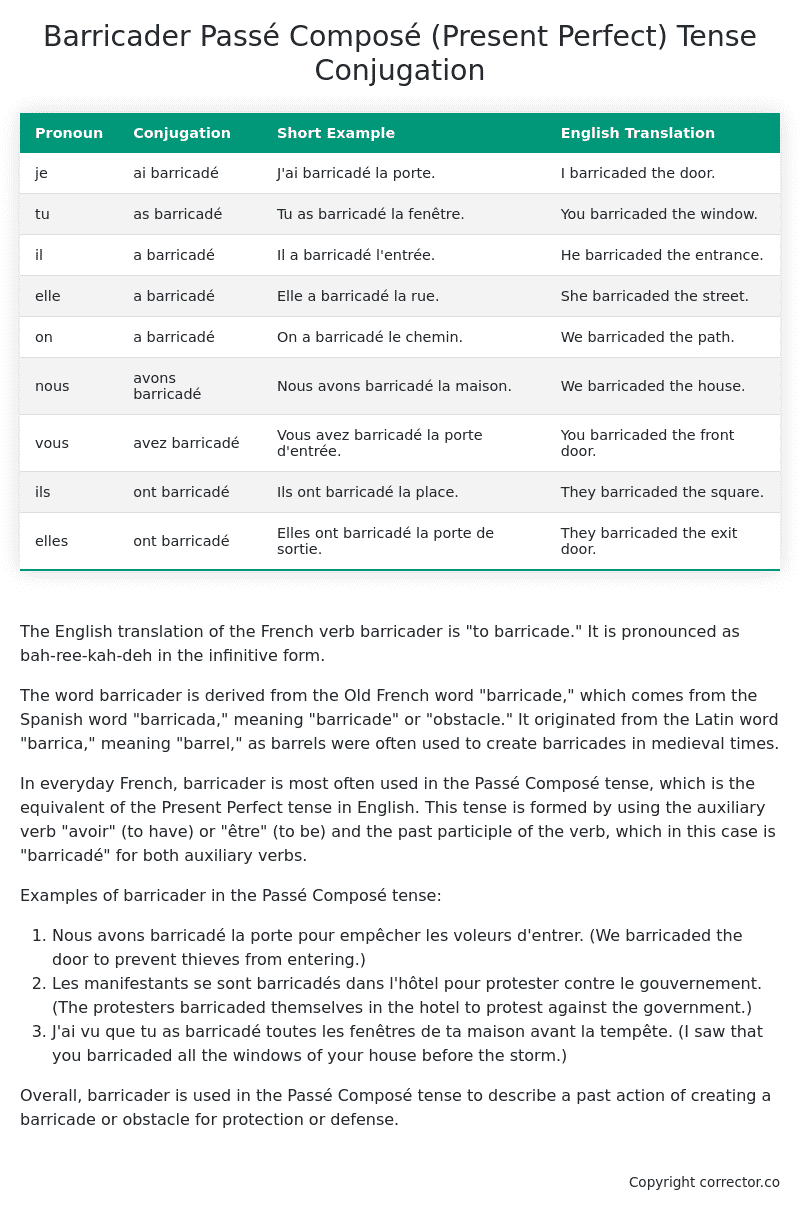
| Pronoun | Conjugation | Short Example | English Translation |
|---|---|---|---|
| je | ai barricadé | J’ai barricadé la porte. | I barricaded the door. |
| tu | as barricadé | Tu as barricadé la fenêtre. | You barricaded the window. |
| il | a barricadé | Il a barricadé l’entrée. | He barricaded the entrance. |
| elle | a barricadé | Elle a barricadé la rue. | She barricaded the street. |
| on | a barricadé | On a barricadé le chemin. | We barricaded the path. |
| nous | avons barricadé | Nous avons barricadé la maison. | We barricaded the house. |
| vous | avez barricadé | Vous avez barricadé la porte d’entrée. | You barricaded the front door. |
| ils | ont barricadé | Ils ont barricadé la place. | They barricaded the square. |
| elles | ont barricadé | Elles ont barricadé la porte de sortie. | They barricaded the exit door. |
Other Conjugations for Barricader.
Le Present (Present Tense) Conjugation of the French Verb barricader
Imparfait (Imperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb barricader
Passé Simple (Simple Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb barricader
Passé Composé (Present Perfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb barricader (this article)
Futur Simple (Simple Future) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb barricader
Futur Proche (Near Future) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb barricader
Plus-que-parfait (Pluperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb barricader
Passé Antérieur (Past Anterior) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb barricader
Futur Antérieur (Future Anterior) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb barricader
Subjonctif Présent (Subjunctive Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb barricader
Subjonctif Passé (Subjunctive Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb barricader
Subjonctif Imparfait (Subjunctive Imperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb barricader
Subjonctif Plus-que-parfait (Subjunctive Pluperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb barricader
Conditionnel Présent (Conditional Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb barricader
Conditionnel Passé (Conditional Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb barricader
L’impératif Présent (Imperative Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb barricader
L’infinitif Présent (Infinitive Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb barricader
Struggling with French verbs or the language in general? Why not use our free French Grammar Checker – no registration required!
Get a FREE Download Study Sheet of this Conjugation 🔥
Simply right click the image below, click “save image” and get your free reference for the barricader present perfect tense conjugation!
Barricader – About the French Passé Composé (Present Perfect) Tense
Formation of the Passé Composé
Set the auxiliary verb with either
Conjugate the auxiliary verb
Add the past participle
Common everyday usage patterns
Narrating Past Events
Sequential Actions
Describing Completed Actions
Interactions with other tenses
Imperfect Tense
Conditional and Future Tenses
Summary
I hope you enjoyed this article on the verb barricader. Still in a learning mood? Check out another TOTALLY random French verb conjugation!


