Plus-que-parfait (Pluperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb calculer
Introduction to the verb calculer
The English translation of the French verb calculer is “to calculate.” It is pronounced as “kah-kyuh-lay.”
The origin of the word calculer comes from the Latin word “calculare,” meaning to count or reckon. In everyday French, it is most often used to refer to the act of performing mathematical calculations or estimations.
In the Plus-que-parfait tense, which is the past perfect tense in English, calculer is used to indicate actions that were completed before a specific point in the past. Here are three simple examples of its usage in this tense:
-
J’avais calculé le montant total avant de partir en vacances. (I had calculated the total amount before leaving for vacation.)
-
Ils s’étaient bien calculé leur trajet et sont arrivés à l’heure à leur rendez-vous. (They had planned their route well and arrived on time for their appointment.)
-
J’avais calculé le temps qu’il me faudrait pour finir mon projet, mais j’ai finalement pris plus de temps que prévu. (I had estimated the amount of time I would need to finish my project, but I ended up taking longer than expected.)
Table of the Plus-que-parfait (Pluperfect) Tense Conjugation of calculer
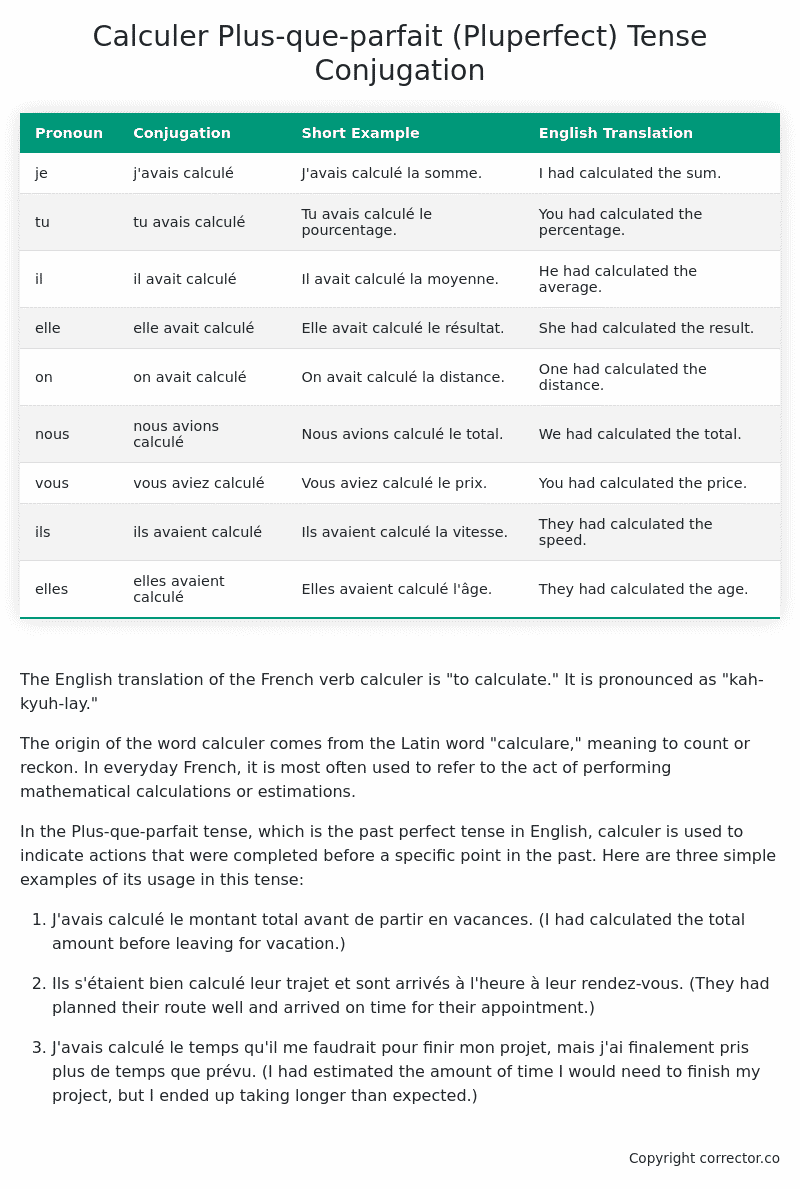
| Pronoun | Conjugation | Short Example | English Translation |
|---|---|---|---|
| je | j’avais calculé | J’avais calculé la somme. | I had calculated the sum. |
| tu | tu avais calculé | Tu avais calculé le pourcentage. | You had calculated the percentage. |
| il | il avait calculé | Il avait calculé la moyenne. | He had calculated the average. |
| elle | elle avait calculé | Elle avait calculé le résultat. | She had calculated the result. |
| on | on avait calculé | On avait calculé la distance. | One had calculated the distance. |
| nous | nous avions calculé | Nous avions calculé le total. | We had calculated the total. |
| vous | vous aviez calculé | Vous aviez calculé le prix. | You had calculated the price. |
| ils | ils avaient calculé | Ils avaient calculé la vitesse. | They had calculated the speed. |
| elles | elles avaient calculé | Elles avaient calculé l’âge. | They had calculated the age. |
Other Conjugations for Calculer.
Le Present (Present Tense) Conjugation of the French Verb calculer
Imparfait (Imperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb calculer
Passé Simple (Simple Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb calculer
Passé Composé (Present Perfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb calculer
Futur Simple (Simple Future) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb calculer
Futur Proche (Near Future) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb calculer
Plus-que-parfait (Pluperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb calculer (this article)
Passé Antérieur (Past Anterior) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb calculer
Futur Antérieur (Future Anterior) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb calculer
Subjonctif Présent (Subjunctive Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb calculer
Subjonctif Passé (Subjunctive Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb calculer
Subjonctif Imparfait (Subjunctive Imperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb calculer
Subjonctif Plus-que-parfait (Subjunctive Pluperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb calculer
Conditionnel Présent (Conditional Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb calculer
Conditionnel Passé (Conditional Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb calculer
L’impératif Présent (Imperative Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb calculer
L’infinitif Présent (Infinitive Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb calculer
Struggling with French verbs or the language in general? Why not use our free French Grammar Checker – no registration required!
Get a FREE Download Study Sheet of this Conjugation 🔥
Simply right click the image below, click “save image” and get your free reference for the calculer Plus-que-parfait tense conjugation!
Calculer – About the French Plus-que-parfait (Pluperfect) Tense
Tense Formation
Common everyday usage patterns
Sequencing of past events
Background information
Hypothetical or reported speech
Interactions with other tenses
Summary
I hope you enjoyed this article on the verb calculer. Still in a learning mood? Check out another TOTALLY random French verb conjugation!


