Plus-que-parfait (Pluperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb déchaperonner
Introduction to the verb déchaperonner
The English translation of the French verb déchaperonner is “to unhood,” or “to take off the hood.” It is pronounced as “day-shah-peh-roh-nay.”
Déchaperonner is derived from the French word “chaperon,” which means hood or capuchin. The prefix “dé-” added to it means “to remove” or “to take off.” It is most commonly used in everyday French in the Plus-que-parfait tense, which is the past perfect tense.
In the Plus-que-parfait tense, déchaperonner is used to describe an action that was completed before another past action. For example:
- J’avais déchaperonné mon manteau avant de sortir. (I had unhooded my coat before going out.)
- Elle avait déchaperonné le bébé pour le bercer. (She had taken off the hood of the baby to rock him.)
- Nous avions déchaperonné le moteur pour le réparer. (We had removed the hood of the engine to repair it.)
As seen in these examples, déchaperonner is used with the auxiliary verb “avoir” in the Plus-que-parfait tense. It is often used in the context of preparing or getting ready for an action.
Table of the Plus-que-parfait (Pluperfect) Tense Conjugation of déchaperonner
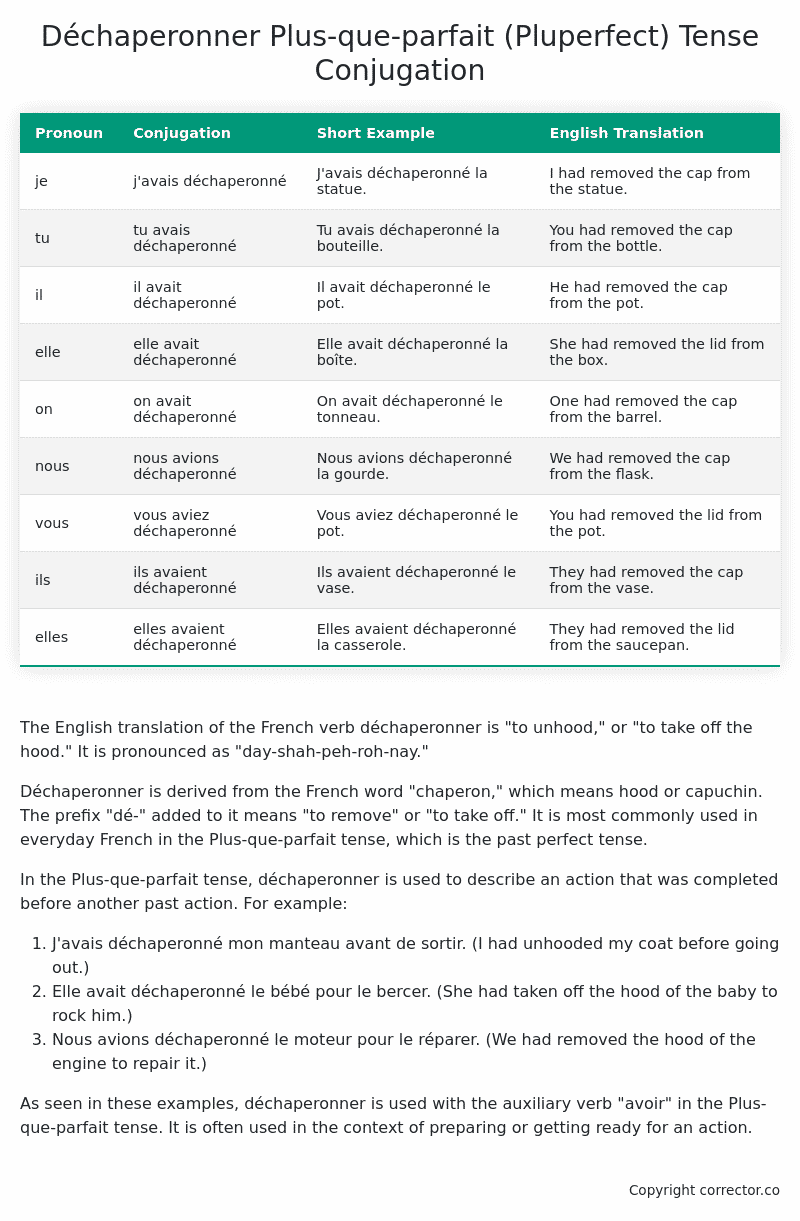
| Pronoun | Conjugation | Short Example | English Translation |
|---|---|---|---|
| je | j’avais déchaperonné | J’avais déchaperonné la statue. | I had removed the cap from the statue. |
| tu | tu avais déchaperonné | Tu avais déchaperonné la bouteille. | You had removed the cap from the bottle. |
| il | il avait déchaperonné | Il avait déchaperonné le pot. | He had removed the cap from the pot. |
| elle | elle avait déchaperonné | Elle avait déchaperonné la boîte. | She had removed the lid from the box. |
| on | on avait déchaperonné | On avait déchaperonné le tonneau. | One had removed the cap from the barrel. |
| nous | nous avions déchaperonné | Nous avions déchaperonné la gourde. | We had removed the cap from the flask. |
| vous | vous aviez déchaperonné | Vous aviez déchaperonné le pot. | You had removed the lid from the pot. |
| ils | ils avaient déchaperonné | Ils avaient déchaperonné le vase. | They had removed the cap from the vase. |
| elles | elles avaient déchaperonné | Elles avaient déchaperonné la casserole. | They had removed the lid from the saucepan. |
Other Conjugations for Déchaperonner.
Le Present (Present Tense) Conjugation of the French Verb déchaperonner
Imparfait (Imperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb déchaperonner
Passé Simple (Simple Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb déchaperonner
Passé Composé (Present Perfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb déchaperonner
Futur Simple (Simple Future) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb déchaperonner
Futur Proche (Near Future) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb déchaperonner
Plus-que-parfait (Pluperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb déchaperonner (this article)
Passé Antérieur (Past Anterior) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb déchaperonner
Futur Antérieur (Future Anterior) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb déchaperonner
Subjonctif Présent (Subjunctive Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb déchaperonner
Subjonctif Passé (Subjunctive Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb déchaperonner
Subjonctif Imparfait (Subjunctive Imperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb déchaperonner
Conditionnel Présent (Conditional Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb déchaperonner
Conditionnel Passé (Conditional Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb déchaperonner
L’impératif Présent (Imperative Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb déchaperonner
L’infinitif Présent (Infinitive Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb déchaperonner
Struggling with French verbs or the language in general? Why not use our free French Grammar Checker – no registration required!
Get a FREE Download Study Sheet of this Conjugation 🔥
Simply right click the image below, click “save image” and get your free reference for the déchaperonner Plus-que-parfait tense conjugation!
Déchaperonner – About the French Plus-que-parfait (Pluperfect) Tense
Tense Formation
Common everyday usage patterns
Sequencing of past events
Background information
Hypothetical or reported speech
Interactions with other tenses
Summary
I hope you enjoyed this article on the verb déchaperonner. Still in a learning mood? Check out another TOTALLY random French verb conjugation!


