Subjonctif Imparfait (Subjunctive Imperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb chiner
Introduction to the verb chiner
The English translation of the French verb chiner is “to hunt for treasures/to go antique hunting”. It is pronounced as “shee-nay”.
The word “chiner” comes from the French word “chine”, which means “china”. In the past, the French word “chine” was often used to refer to any kind of porcelain or ceramic objects, which were highly sought after and considered valuable treasures. Over time, the verb “chiner” emerged to describe the act of searching for and acquiring these treasures.
In everyday French, the verb “chiner” is most often used in the Subjonctif Imparfait tense, which expresses a hypothetical action or a desire in the past. Here are three simple examples of its usage in this tense:
-
Je voulais que tu chinasses avec moi ce week-end. (I wanted you to go antique hunting with me this weekend.)
-
Il fallait que nous chinions dans les brocantes pour trouver un beau cadre. (We had to go hunting for treasures in flea markets to find a beautiful frame.)
-
Mes parents préféraient que je chinasse plutôt que de passer mon temps devant la télé. (My parents preferred me to go antique hunting instead of spending my time in front of the TV.)
Table of the Subjonctif Imparfait (Subjunctive Imperfect) Tense Conjugation of chiner
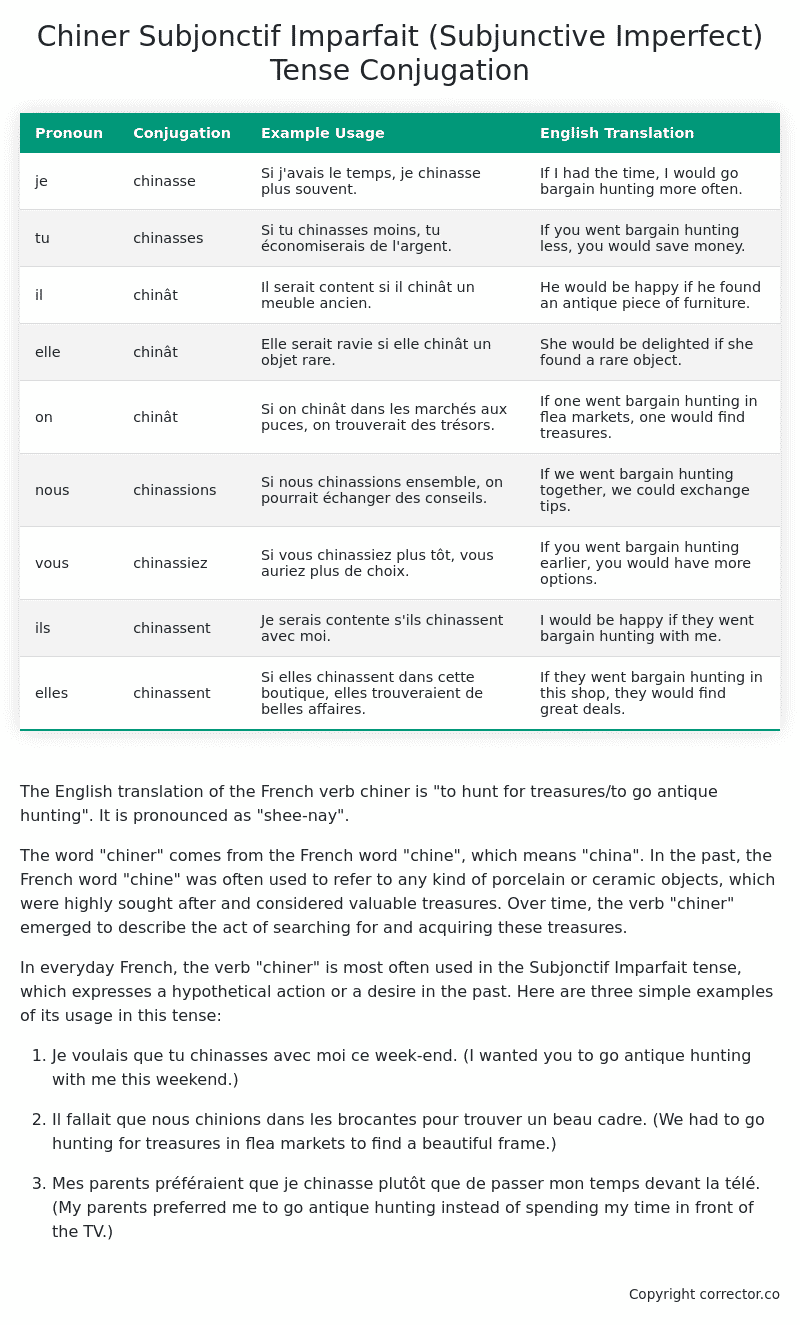
| Pronoun | Conjugation | Example Usage | English Translation |
|---|---|---|---|
| je | chinasse | Si j’avais le temps, je chinasse plus souvent. | If I had the time, I would go bargain hunting more often. |
| tu | chinasses | Si tu chinasses moins, tu économiserais de l’argent. | If you went bargain hunting less, you would save money. |
| il | chinât | Il serait content si il chinât un meuble ancien. | He would be happy if he found an antique piece of furniture. |
| elle | chinât | Elle serait ravie si elle chinât un objet rare. | She would be delighted if she found a rare object. |
| on | chinât | Si on chinât dans les marchés aux puces, on trouverait des trésors. | If one went bargain hunting in flea markets, one would find treasures. |
| nous | chinassions | Si nous chinassions ensemble, on pourrait échanger des conseils. | If we went bargain hunting together, we could exchange tips. |
| vous | chinassiez | Si vous chinassiez plus tôt, vous auriez plus de choix. | If you went bargain hunting earlier, you would have more options. |
| ils | chinassent | Je serais contente s’ils chinassent avec moi. | I would be happy if they went bargain hunting with me. |
| elles | chinassent | Si elles chinassent dans cette boutique, elles trouveraient de belles affaires. | If they went bargain hunting in this shop, they would find great deals. |
Other Conjugations for Chiner.
Le Present (Present Tense) Conjugation of the French Verb chiner
Imparfait (Imperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb chiner
Passé Simple (Simple Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb chiner
Passé Composé (Present Perfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb chiner
Futur Simple (Simple Future) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb chiner
Futur Proche (Near Future) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb chiner
Plus-que-parfait (Pluperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb chiner
Passé Antérieur (Past Anterior) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb chiner
Futur Antérieur (Future Anterior) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb chiner
Subjonctif Présent (Subjunctive Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb chiner
Subjonctif Passé (Subjunctive Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb chiner
Subjonctif Imparfait (Subjunctive Imperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb chiner (this article)
Subjonctif Plus-que-parfait (Subjunctive Pluperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb chiner
Conditionnel Présent (Conditional Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb chiner
Conditionnel Passé (Conditional Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb chiner
L’impératif Présent (Imperative Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb chiner
L’infinitif Présent (Infinitive Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb chiner
Struggling with French verbs or the language in general? Why not use our free French Grammar Checker – no registration required!
Get a FREE Download Study Sheet of this Conjugation 🔥
Simply right click the image below, click “save image” and get your free reference for the chiner Subjonctif Imparfait tense conjugation!
Chiner – About the French Subjonctif Imparfait (Subjunctive Imperfect) Tense
Formation
Common Everyday Usage Patterns
Interactions with Other Tenses
Subjonctif Présent
Indicatif Passé Composé
Conditional
Conditional Perfect
Summary
I hope you enjoyed this article on the verb chiner. Still in a learning mood? Check out another TOTALLY random French verb conjugation!


