Subjonctif Plus-que-parfait (Subjunctive Pluperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb acagnarder
Introduction to the verb acagnarder
The English translation of the French verb acagnarder is “to make someone feel comfortable or cozy”. It is pronounced “ah-kah-nyahr-day.”
The word acagnarder comes from the French word “cagnard,” which means “pleasant and comfortable.” It is most often used in everyday French in the Subjonctif Plus-que-parfait tense, which is used to express actions that are hypothetical or hypothetical events that have already been completed in the past.
Here are three simple examples of how acagnarder can be used in the Subjonctif Plus-que-parfait tense:
-
Je regrettais de ne pas avoir acagnardé ma sœur avant qu’elle ne quitte la maison. (I regretted not making my sister feel comfortable before she left the house.)
-
Mes parents m’avaient acagnardé pour que je me sente mieux après ma rupture. (My parents had made me feel comfortable to help me feel better after my break-up.)
-
Si tu avais acagnardé tes invités, ils n’auraient pas eu froid pendant la soirée. (If you had made your guests feel comfortable, they wouldn’t have been cold during the evening.)
-
I regretted not making my sister feel comfortable before she left the house.
-
My parents had made me feel comfortable to help me feel better after my break-up.
-
If you had made your guests feel comfortable, they wouldn’t have been cold during the evening.
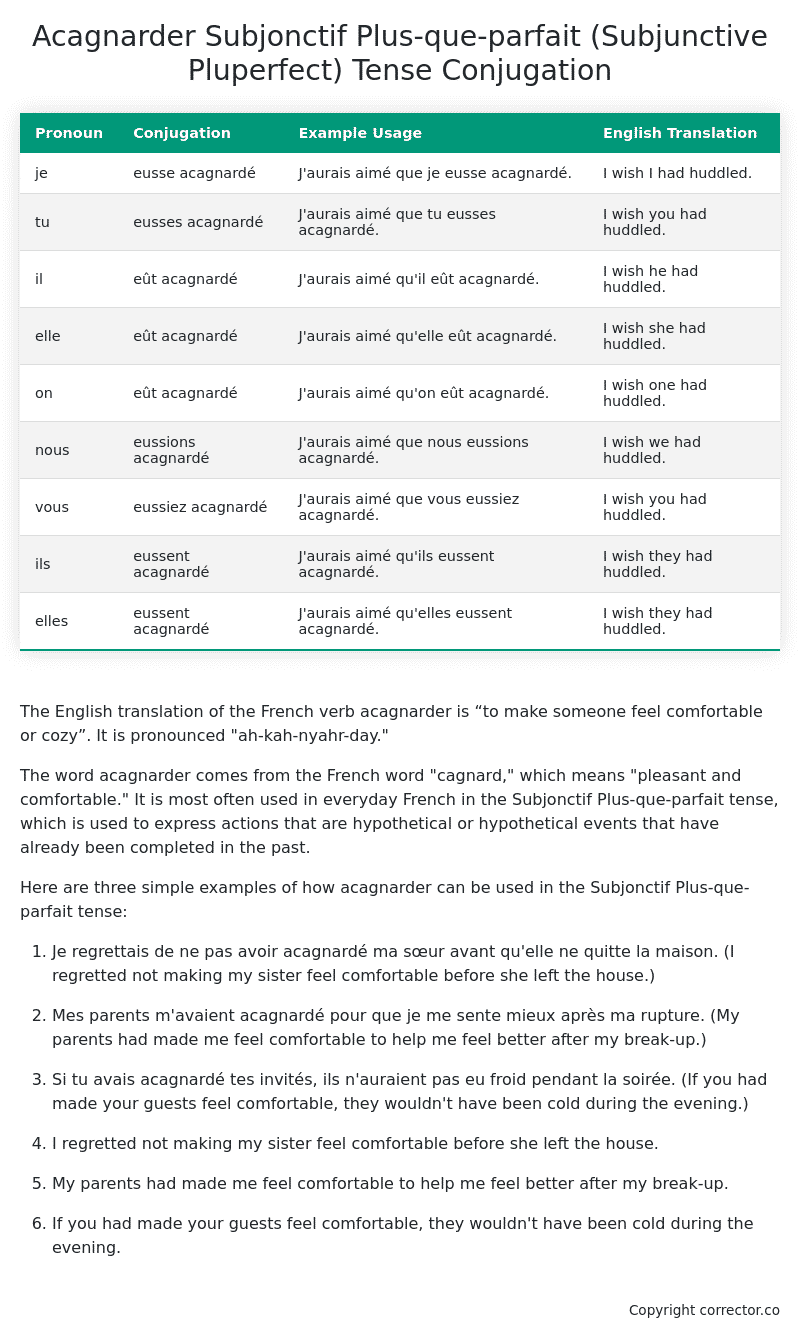
Table of the Subjonctif Plus-que-parfait (Subjunctive Pluperfect) Tense Conjugation of acagnarder
| Pronoun | Conjugation | Example Usage | English Translation |
|---|---|---|---|
| je | eusse acagnardé | J’aurais aimé que je eusse acagnardé. | I wish I had huddled. |
| tu | eusses acagnardé | J’aurais aimé que tu eusses acagnardé. | I wish you had huddled. |
| il | eût acagnardé | J’aurais aimé qu’il eût acagnardé. | I wish he had huddled. |
| elle | eût acagnardé | J’aurais aimé qu’elle eût acagnardé. | I wish she had huddled. |
| on | eût acagnardé | J’aurais aimé qu’on eût acagnardé. | I wish one had huddled. |
| nous | eussions acagnardé | J’aurais aimé que nous eussions acagnardé. | I wish we had huddled. |
| vous | eussiez acagnardé | J’aurais aimé que vous eussiez acagnardé. | I wish you had huddled. |
| ils | eussent acagnardé | J’aurais aimé qu’ils eussent acagnardé. | I wish they had huddled. |
| elles | eussent acagnardé | J’aurais aimé qu’elles eussent acagnardé. | I wish they had huddled. |
Other Conjugations for Acagnarder.
Le Present (Present Tense) Conjugation of the French Verb acagnarder
Imparfait (Imperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb acagnarder
Passé Simple (Simple Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb acagnarder
Passé Composé (Present Perfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb acagnarder
Futur Simple (Simple Future) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb acagnarder
Futur Proche (Near Future) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb acagnarder
Plus-que-parfait (Pluperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb acagnarder
Passé Antérieur (Past Anterior) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb acagnarder
Futur Antérieur (Future Anterior) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb acagnarder
Subjonctif Présent (Subjunctive Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb acagnarder
Subjonctif Passé (Subjunctive Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb acagnarder
Subjonctif Imparfait (Subjunctive Imperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb acagnarder
Subjonctif Plus-que-parfait (Subjunctive Pluperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb acagnarder
Conditionnel Présent (Conditional Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb acagnarder
Conditionnel Passé (Conditional Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb acagnarder
L’impératif Présent (Imperative Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb acagnarder
L’infinitif Présent (Infinitive Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb acagnarder
(this article)
Struggling with French verbs or the language in general? Why not use our free French Grammar Checker – no registration required!
Get a FREE Download Study Sheet of this Conjugation 🔥
Simply right click the image below, click “save image” and get your free reference for the acagnarder Subjonctif Plus-que-parfait tense conjugation!
Acagnarder – About the French Subjonctif Plus-que-parfait (Subjunctive Pluperfect) Tense
Formation
Common Everyday Usage Patterns
Hypothetical Situations
Reported Speech
Doubt, Wishes, and Emotions
Interactions with Other Tenses
Present Subjunctive
Imperfect Subjunctive
Conditional
Summary
I hope you enjoyed this article on the verb acagnarder. Still in a learning mood? Check out another TOTALLY random French verb conjugation!


