Subjonctif Plus-que-parfait (Subjunctive Pluperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb différentier
Introduction to the verb différentier
The English translation of the French verb différentier is “to differentiate.” It is pronounced “dee-fuh-rayn-tee-ey.”
The origin of différentier can be traced back to the Latin word “differentiare,” meaning “to distinguish.” It is most often used in everyday French to express the action of distinguishing or differentiating between two or more things.
In the Subjonctif Plus-que-parfait tense, différentier is used to express a hypothetical past action that was completed before another past action. It is formed by conjugating the auxiliary verb “avoir” in the Subjonctif Imparfait (avais, avais, avait, avions, aviez, avaient) and adding the past participle of différentier (différentié).
Here are three simple examples of différentier in the Subjonctif Plus-que-parfait tense with their respective English translations:
- J’avais différencié les deux espèces avant que tu ne m’en parles.
(I had differentiated the two species before you told me about them.) - Elle avait différencié les trois saveurs avant de choisir sa préférée.
(She had differentiated the three flavors before choosing her favorite one.) - Nous avions différencié les différentes teintes de bleu avant que le professeur ne nous en demande la raison.
(We had differentiated the different shades of blue before the teacher asked us about the reason behind it.)
Table of the Subjonctif Plus-que-parfait (Subjunctive Pluperfect) Tense Conjugation of différentier
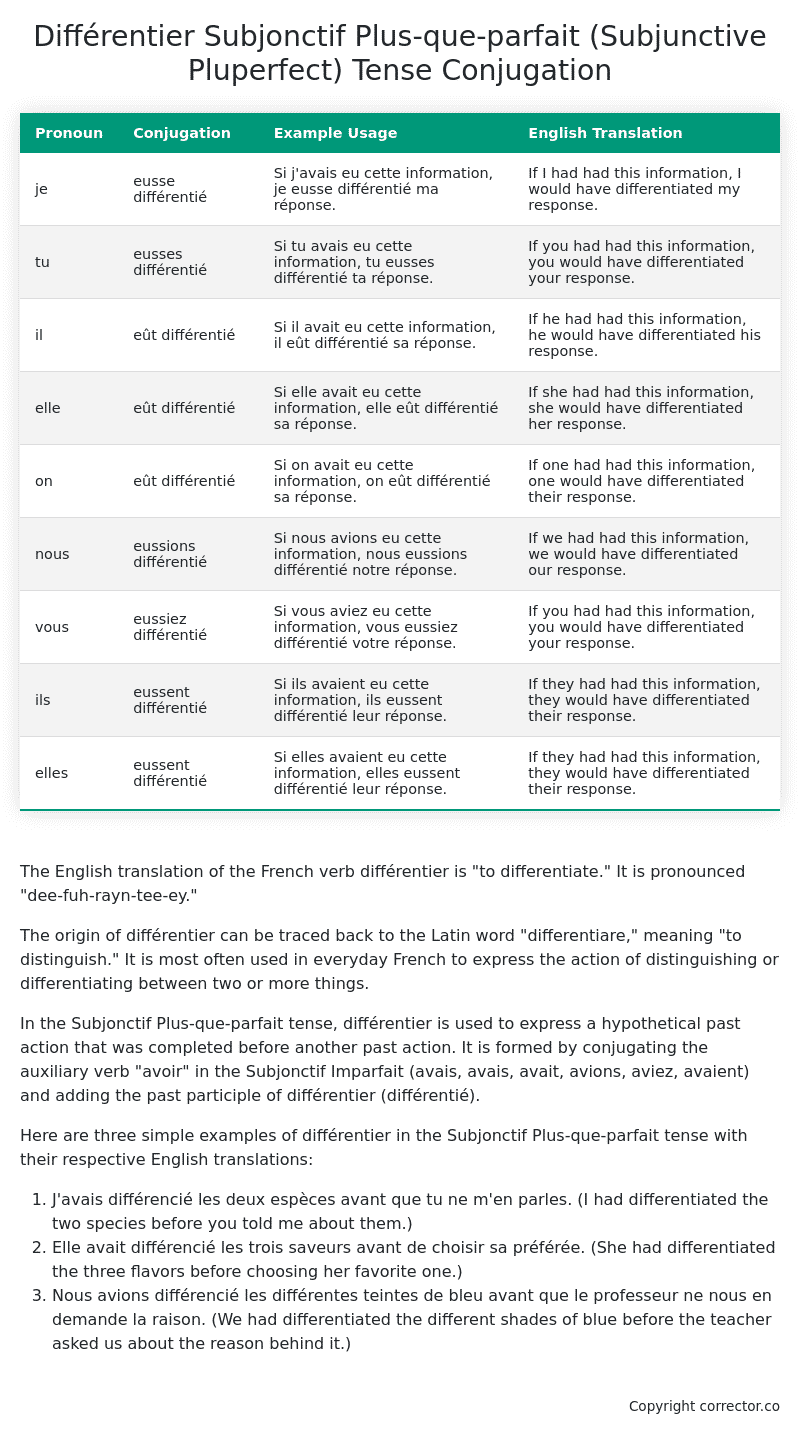
| Pronoun | Conjugation | Example Usage | English Translation |
|---|---|---|---|
| je | eusse différentié | Si j’avais eu cette information, je eusse différentié ma réponse. | If I had had this information, I would have differentiated my response. |
| tu | eusses différentié | Si tu avais eu cette information, tu eusses différentié ta réponse. | If you had had this information, you would have differentiated your response. |
| il | eût différentié | Si il avait eu cette information, il eût différentié sa réponse. | If he had had this information, he would have differentiated his response. |
| elle | eût différentié | Si elle avait eu cette information, elle eût différentié sa réponse. | If she had had this information, she would have differentiated her response. |
| on | eût différentié | Si on avait eu cette information, on eût différentié sa réponse. | If one had had this information, one would have differentiated their response. |
| nous | eussions différentié | Si nous avions eu cette information, nous eussions différentié notre réponse. | If we had had this information, we would have differentiated our response. |
| vous | eussiez différentié | Si vous aviez eu cette information, vous eussiez différentié votre réponse. | If you had had this information, you would have differentiated your response. |
| ils | eussent différentié | Si ils avaient eu cette information, ils eussent différentié leur réponse. | If they had had this information, they would have differentiated their response. |
| elles | eussent différentié | Si elles avaient eu cette information, elles eussent différentié leur réponse. | If they had had this information, they would have differentiated their response. |
Other Conjugations for Différentier.
Le Present (Present Tense) Conjugation of the French Verb différentier
Imparfait (Imperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb différentier
Passé Simple (Simple Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb différentier
Passé Composé (Present Perfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb différentier
Futur Simple (Simple Future) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb différentier
Futur Proche (Near Future) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb différentier
Plus-que-parfait (Pluperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb différentier
Passé Antérieur (Past Anterior) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb différentier
Futur Antérieur (Future Anterior) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb différentier
Subjonctif Présent (Subjunctive Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb différentier
Subjonctif Passé (Subjunctive Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb différentier
Subjonctif Imparfait (Subjunctive Imperfect) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb différentier
Conditionnel Présent (Conditional Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb différentier
Conditionnel Passé (Conditional Past) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb différentier
L’impératif Présent (Imperative Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb différentier
L’infinitif Présent (Infinitive Present) Tense Conjugation of the French Verb différentier
(this article)
Struggling with French verbs or the language in general? Why not use our free French Grammar Checker – no registration required!
Get a FREE Download Study Sheet of this Conjugation 🔥
Simply right click the image below, click “save image” and get your free reference for the différentier Subjonctif Plus-que-parfait tense conjugation!
Différentier – About the French Subjonctif Plus-que-parfait (Subjunctive Pluperfect) Tense
Formation
Common Everyday Usage Patterns
Hypothetical Situations
Reported Speech
Doubt, Wishes, and Emotions
Interactions with Other Tenses
Present Subjunctive
Imperfect Subjunctive
Conditional
Summary
I hope you enjoyed this article on the verb différentier. Still in a learning mood? Check out another TOTALLY random French verb conjugation!


